FLUİD BED DRYER/CHİLLER
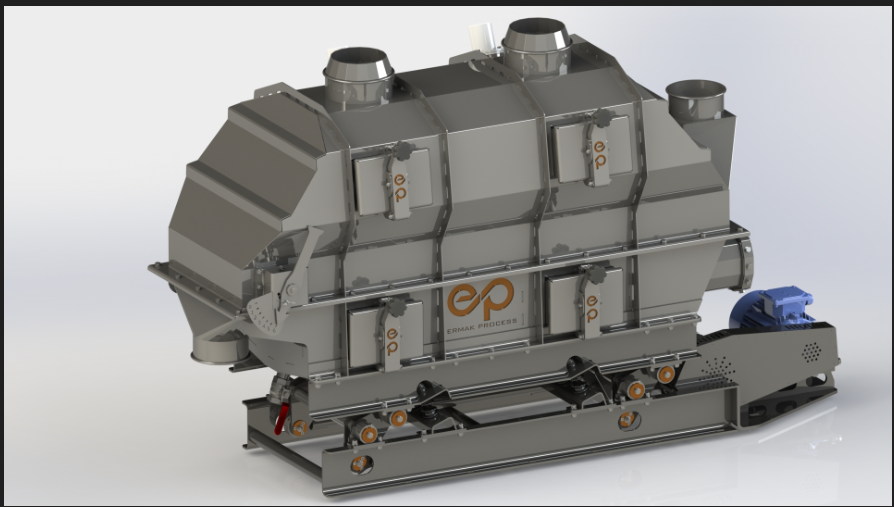
### Fluid Bed Roaster
Overview
The fluid bed roaster operates on the principle of keeping solid particles suspended by sending air at a speed and pressure that overcomes gravitational forces. This is achieved by directing pressurized air through a dispersing plate with specially designed holes, creating a flow that supports the weight of the particles. As air passes through the solids bed, it forms and precipitates bubbles, promoting intense particle movement and causing the solids to behave like a boiling liquid. This fluidized state ensures extremely high heat and mass transfer due to the close contact and differential velocities between the particles and the fluidizing gas.
### Types of Fluid Bed Dryers
1. **Vibratory Fluid Bed Dryer**: Uses vibrations to enhance fluidization and particle movement.
2. **Shaking Fluid Bed Dryer**: Employs a shaking mechanism to assist in fluidization and uniform drying.
3. **Static Fluid Bed Dryer**: Relies solely on fluidizing air without additional mechanical assistance.
4. **Batch Fluid Bed Dryer**: Processes materials in discrete batches, allowing for controlled and uniform drying.
### Application Areas
- **Low Energy Consumption**:
Fluid bed dryers consume less energy compared to other drying technologies, making them cost-effective.
- **Versatile Energy Sources**: These systems can utilize different fuel types, providing flexibility in energy supply.
- **Simultaneous Cooling**: Some fluid bed dryers can cool the material concurrently with the drying process.
- **Fast and Uniform Heat Transfer**: The fluidized state ensures rapid and even distribution of heat throughout the material.
- **Short Drying Time**: Enhanced heat and mass transfer rates result in quicker drying cycles.
- **Wide Range of Particle Sizes**: Capable of drying products with particle sizes ranging from 50 microns to 5 mm.
- **Low to Medium Temperature Drying**: Suitable for materials that require drying at lower and moderate temperatures.
### Summary
Fluid bed roasters utilize fluidization principles to suspend and agitate particles through pressurized air, achieving high heat and mass transfer efficiencies. The various types of fluid bed dryers, including vibratory, shaking, static, and batch dryers, offer versatility in application. They are known for their low energy consumption, ability to use different fuel sources, simultaneous cooling capabilities, fast and uniform heat transfer, short drying times, and the ability to handle a wide range of particle sizes and temperatures. These features make fluid bed roasters and dryers highly efficient and adaptable for various industrial applications.
ROTARY DRYER/COOLER
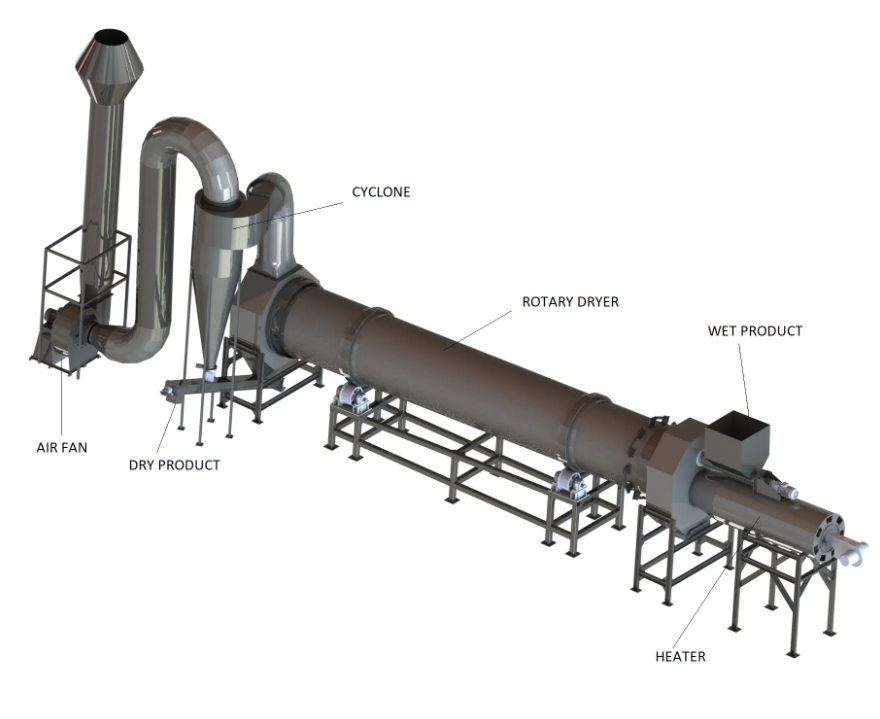
### Rotating Cylinder Dryer
Overview
A rotating cylinder dryer consists of a gently inclined, rotating cylinder installed with a series of peripheral flow lines designed to lift, distribute, and transfer the material being processed. These flow lines are tailored to the specific characteristics of the material, accommodating variations in dryness as the process progresses.
The operational principle involves wetting the material or cascading it along a stream of hot gas, which may flow in the same or opposite direction as the solids. The hot gas induces moisture evaporation from the material, and the heat transfer to the material, combined with the evaporation of water, quickly lowers the temperature of the gas, which exits the dryer at a relatively lower temperature. Rotary coolers operate similarly to dryers but always with a reverse flow.
They use ambient or chilled air instead of hot gases, making them suitable for low-temperature applications, coarse products, or in combination with an indirect cooling system.
These systems are versatile and efficient for a variety of industrial applications.
### Types of Rotating Cylinder Dryers
1. **Chain Driven**:
Utilizes a chain mechanism to rotate the cylinder, providing robust and reliable operation.
2. **Galley Driven**: Employs a galley drive system for cylinder rotation, offering smooth and efficient motion.
3. **Single-Pass**: The material passes through the cylinder once, typically used for straightforward drying processes.
4. **Double-Pass**: The material passes through the cylinder twice, allowing for more controlled and thorough drying.
### Application Areas
- **Drying Larger Particles**: Suitable for drying products with particle sizes ranging from 5 to 20 mm and above.
- **High-Temperature Operation**: Capable of working at elevated temperatures, making it ideal for heat-intensive processes.
- **Versatile Energy Sources**: Adaptable to various energy sources, enhancing flexibility in operation.
- **High Efficiency**: Provides maximum mixing opportunities with its specially designed blade form, ensuring efficient drying compared to counterparts.
### Summary
Rotating cylinder dryers are efficient and versatile drying systems designed to handle a variety of materials by leveraging hot gas to evaporate moisture. The design features a rotating, inclined cylinder with flow lines to facilitate material movement and drying. These dryers operate on principles similar to rotary coolers, which use ambient or chilled air for cooling purposes. Available in chain-driven, galley-driven, single-pass, and double-pass configurations, rotating cylinder dryers are suitable for drying large particles, operating at high temperatures, and adapting to various energy sources. Their high efficiency and flexibility make them suitable for diverse industrial applications.
JETPULSE FİLTER
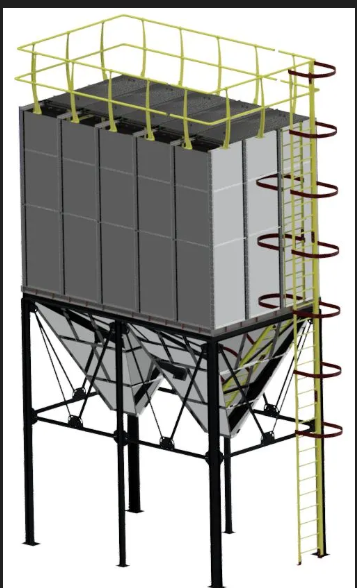
### Jet Pulse Filters
Overview
Jet Pulse filters, also known as bag filters, are automatic filtration systems designed to filter dust, odor, and smoke generated during industrial production through air suction.
These systems are essential for maintaining air quality and ensuring a safe working environment in various industrial settings. The filtration process involves dusty air being taken into the filter through air ducts, where it passes through the outer surface of the filter bags. As the air moves from the outer surface into the filter, dust particles are trapped on the filter surface.
The accumulated dust on the filter bags is periodically removed by blowing compressed air in the opposite direction to the airflow using pulse valves controlled by a timer. This process dislodges the dust, which then falls into a conical section under the filter body.
The collected dust can be removed using various systems such as buckets, big-bags, conveyors, or augers, depending on the specific needs and location.
### Key Features and Design Considerations
- **Filter Bags**:
Designed based on parameters such as operating temperature, dust particle size, and density.
- **Modular Design**: Jet Pulse filters are modularly designed and manufactured to meet specific capacity and operational requirements.
- **Dust Collection**: Dust dislodged from the filter bags is collected in the cone and can be removed using different collection systems based on the application.
### Benefits
- **Efficient Filtration**: Effective removal of dust, odors, and smoke, improving air quality.
- **Automatic Operation**: The automatic cleaning mechanism ensures continuous and efficient operation.
- **Customizable**: Can be tailored to meet specific industrial requirements, ensuring optimal performance.
- **Versatile Dust Collection**: Multiple options for dust collection and disposal enhance flexibility and convenience.
### Request a Quote for Jet Pulse Filters
To request a quote for a Jet Pulse filter tailored to your requirements, please provide the following details:
1. **Operating Conditions**:
- Operating temperature
- Type and size of dust particles
- Dust density
2. **Capacity Requirements**:
- Airflow rate (in cubic meters per hour or cubic feet per minute)
- Volume of dust to be handled
3. **Design Specifications**:
- Preferred type of dust collection system (buckets, big-bags, conveyors, augers, etc.)
- Space available for installation
- Any specific modular design preferences
4. **Additional Requirements**:
- Specific industry regulations or standards to comply with
- Any additional features or customization needed
### Summary
Jet Pulse filters are essential for maintaining clean air in industrial environments, efficiently removing dust, odors, and smoke. Their automatic cleaning mechanism and customizable design make them suitable for a wide range of applications. By providing detailed operating conditions, capacity requirements, and design specifications, you can receive a tailored quote for a Jet Pulse filter that meets your specific needs.
HEAT EXCHANGER
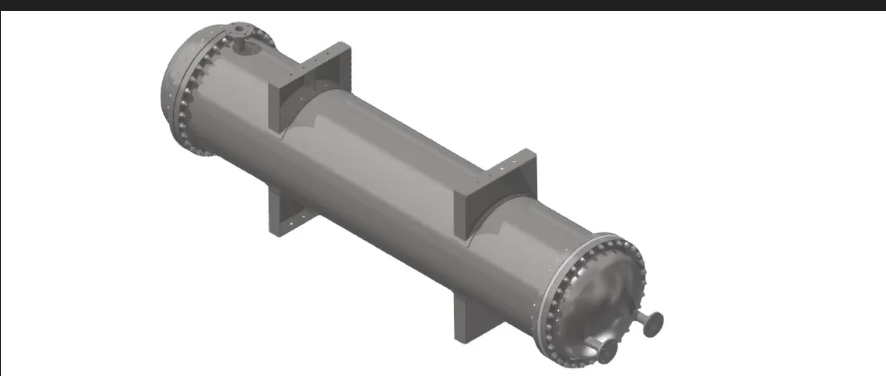
### Heat Exchangers
Overview
Heat exchangers are essential pieces of equipment in the process industry, used for heating, cooling, and evaporation of liquids, gases, and solids in precise amounts. They are designed to transfer heat between different media, ensuring efficient temperature control in various industrial processes. Our production capabilities include a variety of heat exchangers tailored for specific usage purposes.
### Types of Heat Exchangers
1. **TEMA Type Tubular Heat Exchangers**:
These are built to the standards set by the Tubular Exchanger Manufacturers Association (TEMA), offering reliability and efficiency for various industrial applications.
2. **Fin Tube Heat Exchangers**:
These are designed with extended surfaces to enhance heat transfer between fluids and gases.
3. **Plate Type Powder or Granular Product Heat Exchangers**:
Ideal for handling granular or powdered materials, ensuring efficient heat exchange without product contamination.
4. **Double Pipe Heat Exchangers**:
.Comprising two concentric pipes, these exchangers are suitable for high-temperature and high-pressure applications.
5. **Reboilers**:
Specialized heat exchangers used in distillation processes to provide the necessary heat for vaporizing the liquid mixture.
### Materials of Construction
Our heat exchangers are manufactured from high-quality materials to ensure durability and performance under various operating conditions. The materials used include:
- Carbon steel
- AISI304 stainless steel
- AISI316 stainless steel
- Duplex stainless steel
- Super Duplex stainless steel
- Titanium
### Quality Assurance
The production of our heat exchangers adheres to stringent quality standards within the framework of the Inspection and Test Plan (ITP). This ensures that each unit meets the highest quality criteria. If requested, third-party inspections can be arranged, and detailed reports will be provided to the relevant stakeholders.
### Summary
Our range of heat exchangers is designed to meet the diverse needs of the process industry, ensuring efficient heat transfer for heating, cooling, and evaporation applications. From TEMA type tubular heat exchangers to plate type heat exchangers for powders and granular products, we offer solutions crafted from premium materials such as carbon steel, AISI304, AISI316, Duplex, Super Duplex, and titanium. Adhering to strict quality standards and offering third-party inspections, we ensure that our heat exchangers deliver optimal performance and reliability in any industrial setting.
EVAPORATOR
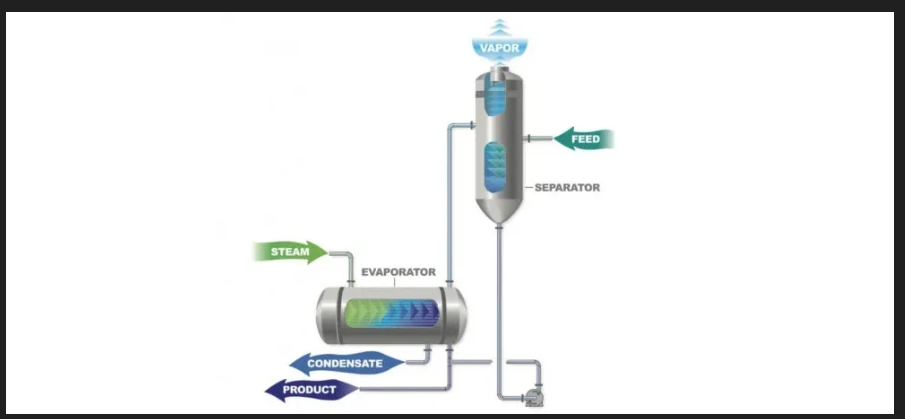
### Multistage Evaporation
Multistage evaporation is an efficient method recommended when low-cost, low-pressure steam is available. This classic technique is widely used for concentrating liquids or obtaining crystals.
The principle involves transferring the steam from one stage to the heater body of the subsequent stage, thereby saving energy. In practical applications, systems can include up to six stages. Increasing the number of stages reduces the amount of fresh steam required, though it raises the initial investment costs. The optimal design balances production and investment costs. Additionally, preheating the feed solution before introducing it into the system can significantly reduce steam consumption in the evaporators.
### Mechanical Vapor Compression (MVR)
The MVR system is ideal for areas where electricity is relatively inexpensive. This system utilizes a radial turbo compressor or an industrial fan to compress the steam produced in the evaporator, increasing its pressure and temperature for reuse.
The advantages of MVR systems include:
- **Minimal Fresh Steam Requirement**: Since the steam is compressed and reused, fresh steam is only needed during the initial commissioning phase.
- **No Cooling Water Requirement**: The system's design eliminates the need for cooling water, further enhancing efficiency.
- **Low Construction Costs**: The compact design of MVR systems results in lower construction costs.
- **Ease of Operation**: MVR systems are straightforward to commission and operate, making them user-friendly and reliable.
### Summary
Multistage evaporation and mechanical vapor compression (MVR) are both effective methods for concentrating liquids and obtaining crystals, each with specific advantages. Multistage evaporation is energy-efficient and ideal when low-cost steam is available, utilizing multiple stages to reduce steam consumption and optimize energy use.
In contrast, MVR systems are recommended for regions with low electricity costs, compressing and reusing steam to eliminate the need for fresh steam and cooling water, while also benefiting from a compact and cost-effective design. Both systems offer significant operational efficiencies and can be tailored to balance production costs and investment.
### Thermal Vapor Compression (TVR)
Thermal Vapor Compression (TVR) is a method used to increase the temperature and pressure of steam generated in the evaporator through the use of a steam ejector. This steam is then reused in the heat exchanger connected to the evaporator.
In a TVR system, approximately 50% of the steam from the first stage can be effectively reused, while the remaining 50% is directed to the heat exchanger of the second-stage evaporator/condenser.
By incorporating additional steam ejectors and stages, the system can further enhance energy savings and efficiency.
### Advantages of the TVR System
1. **Low Investment Costs**: The TVR system is cost-effective to implement, making it an attractive option for various industrial applications.
2. **Ease of Operation**: The system is straightforward to operate, requiring minimal technical expertise.
3. **Low Maintenance Requirements**:
With no moving parts, the TVR system significantly reduces maintenance costs and downtime.
### Summary
Thermal Vapor Compression (TVR) is a highly efficient system for reusing steam generated in evaporators by increasing its temperature and pressure with a steam ejector. This method allows for substantial energy savings, especially when additional stages and ejectors are incorporated into the system. Key advantages of the TVR system include low investment costs, ease of operation, and minimal maintenance requirements due to the absence of moving parts. These benefits make TVR an attractive solution for industries seeking cost-effective and efficient evaporation processes.
PYROLYSİS SYSTEMS

An Overview
### Pyrolysis:
Pyrolysis is a thermochemical process that involves the chemical decomposition of organic (carbon-based) materials through the application of heat. This process can be applied to any organic material, exposing it to very high temperatures, which leads to chemical and physical decomposition into various molecules in the absence of oxygen. The rate of pyrolysis increases with temperature, and it fundamentally alters the chemical composition of the material, making the end products different from the initial reactants. The term 'pyrolysis' is derived from the Greek words meaning "fire" and "separating."
During pyrolysis, organic materials decompose into a myriad of compounds, resulting in the formation of new products.
This decomposition process can produce solids (rich in carbon), liquids (known as tar), and gases. Industrial applications typically use temperatures of 430°C or higher, while lower temperatures may suffice for small-scale processes.
Pyrolysis is notably distinct from other high-temperature processes like hydrolysis and combustion, as it does not involve reactions with water or oxygen. However, completely oxygen-free environments are challenging to maintain, so minimal oxidation often occurs.
Pyrolysis serves as a precursor to other processes such as combustion and gasification and can yield multiple volatile products and a carbon-rich solid residue.
### Types of Pyrolysis
There are three main types of pyrolysis, each characterized by different conditions and outcomes:
1. **Slow Pyrolysis**: Characterized by long residence times for solids and gases, low temperatures, and slow heating rates. This type modifies solid materials while minimizing oil production.
- **Temperature**: Medium-high (400-500°C)
- **Residence Time**: Long (5-30 minutes)
2. **Rapid Pyrolysis**: Involves the quick thermal decomposition of carbon-containing materials at moderate to high heating rates. The primary product is bio-oil.
- **Temperature**: Medium-high (400-650°C)
- **Residence Time**: Short (0.5-2 seconds)
3. **Flash Pyrolysis**: A very fast process with high heating rates, primarily producing gases and bio-oil. It results in smaller amounts of gas and tar compared to slow pyrolysis.
- **Temperature**: High (700-1000°C) - **Residence Time**: Very short (less than 0.5 seconds)
### Applications of Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis has a wide range of applications across various industries:
- **Renewable Energy**: Converts biomass into liquid fuels with high energy density and produces chemicals from bio-based sources.
- **Waste Management**: Reduces waste and greenhouse gas emissions, offering an economical alternative to landfill disposal.
- **Industrial Processes**: Used for producing activated carbon, charcoal, synthetic gas, and methanol. It also aids in extracting coke and coal ash from coal through destructive distillation.
- **Cooking Techniques**: Common in grilling, frying, roasting, and caramelizing sugar.
- **Construction**: Byproducts can be used as building materials or landfill covers.
- **Scientific Applications**: Employed in carbon-14 dating and mass spectrometry.
### Pyrolysis:
Environmental and Economic Benefits
The pyrolysis process offers several environmental and economic advantages. It enables the use of renewable resources and reduces dependency on external energy sources by producing energy domestically.
The technology is simple, inexpensive, and capable of processing a wide variety of raw materials, making it accessible and practical. Pyrolysis also helps reduce water pollution risks and greenhouse gas emissions. Economically, it creates job opportunities, particularly in waste management sectors, and the construction of pyrolysis plants is relatively quick and cost-effective. Overall, pyrolysis stands out as a sustainable and economically profitable solution for large-scale waste minimization and resource conversion.
We pay $10 for a google review and We are looking for partnerships with other businesses for Google Review Exchange. Please contact us for more information!
Business Name: Sparkly Maid NYC Cleaning Services
Address: 47 Broadway 2nd floor #523, New York, NY 10013, United States
Phone Number: +1 646-585-3515
Website: https://maps.app.goo.gl/u9iJ9RnactaMEEie8
We pay $10 for a google review and We are looking for partnerships with other businesses for Google Review Exchange. Please contact us for more information!
Business Name: Sparkly Maid NYC Cleaning Services
Address: 447 Broadway 2nd floor #523, New York, NY 10013, United States
Phone Number: +1 646-585-3515
Website: https://maps.app.goo.gl/u9iJ9RnactaMEEie8
We pay $10 for a google review and We are looking for partnerships with other businesses for Google Review Exchange. Please contact us for more information!
Business Name: Sparkly Maid NYC Cleaning Services
Address: 447 Broadway 2nd floor #523, New York, NY 10013, United States
Phone Number: +1 646-585-3515
Website: https://maps.app.goo.gl/u9iJ9RnactaMEEie8
We pay $10 for a google review and We are looking for partnerships with other businesses for Google Review Exchange. Please contact us for more information!
Business Name: Sparkly Maid NYC Cleaning Services
Address: 447 Broadway 2nd floor #523, New York, NY 10013, United States
Phone Number: +1 646-585-3515
Website: https://maps.app.goo.gl/u9iJ9RnactaMEEie8
We pay $10 for a google review and We are looking for partnerships with other businesses for Google Review Exchange. Please contact us for more information!
Business Name: Sparkly Maid NYC Cleaning Services
Address: 447 Broadway 2nd floor #523, New York, NY 10013, United States
Phone Number: +1 646-585-3515
Website: https://sparklymaidnyc.com
We pay $10 for a google review and We are looking for partnerships with other businesses for Google Review Exchange. Please contact us for more information!
Business Name: Sparkly Maid NYC Cleaning Services
Address: 447 Broadway 2nd floor #523, New York, NY 10013, United States
Phone Number: +1 646-585-3515
Website: https://sparklymaidnyc.com
We pay $10 for a google review and We are looking for partnerships with other businesses for Google Review Exchange. Please contact us for more information!
Business Name: Sparkly Maid NYC Cleaning Services
Address: 447 Broadway 2nd floor #523, New York, NY 10013, United States
Phone Number: +1 646-585-3515
Website: https://sparklymaidnyc.com
There is visibly a lot to realize about this. I assume you made certain good points in features also.
This is my first time go to seee at here and i am truly pleassant to read everthing at single place. https://Jgew1.mssg.me/
Amazing Brooklyn crew, knows exactly what Park Slope needs. Booking for our whole building. Great local business.
Performance perfection achieved, performance matches the promises. Outcome-driven professionals. Performance excellence.
I all the time emailed this webpage post page to all my contacts, as
if like to read it afterward my contacts will too.
Feel free to visit my web blog; nordvpn coupons inspiresensation [tinyurl.com]
I enjoy what you guys are usually up too. This sort of clever work
and coverage! Keep up the amazing works guys I’ve incorporated you guys to blogroll.
Feel free too visit my webpage :: https://sites.Google.com/view/gambling-gamingindustry
I have been checking out some of your stories and i can claim clever stuff. I will surely bookmark your site.
Hi! I know this is kind of off topic but I was wondering if you knew where I could get a captcha plugin for my comment form? I’m using the same blog platform as yours and I’m having trouble finding one? Thanks a lot!
Hi there, You have done an incredible job. I’ll certainly digg it and personally suggest to my friends. I’m confident they’ll be benefited from this web site.
It?¦s really a cool and useful piece of information. I am satisfied that you shared this useful information with us. Please stay us up to date like this. Thank you for sharing.
This is very fascinating, You’re an overly skilled blogger. I have joined your rss feed and look ahead to seeking more of your great post. Also, I’ve shared your website in my social networks!
Good day! I know this is kind of off topic but I was wondering which blog platform are you using for this site? I’m getting tired of WordPress because I’ve had problems with hackers and I’m looking at options for another platform. I would be awesome if you could point me in the direction of a good platform.
I am using word press
I wanted to thank you for this great read!! I definitely enjoying every little bit of it I have you bookmarked to check out new stuff you post…
Its only a pleasure. Glad you liked the info.
It’s going to be ending of mіne day, exϲept before ending
I am reading this impressive piecе of writing to increase my know-һow.
Thank you for your kind words. It really makes a difference.
I was studying some of your content on this website and I believe this web site is real informative! Retain putting up.