Introduction
### Types of Conveyors in Mineral Processing
1. **Belt Conveyors**:
- **Function**:
Primarily used for transporting bulk materials over long distances.
- **Applications**:
Ideal for conveying raw materials from the mine to the processing plant, or between different stages of the processing plant.
- **Advantages**:
High efficiency, low operating cost, and the ability to handle large volumes of materials.
2. **Apron Conveyors**:
- **Function**:
Designed to handle heavy, abrasive materials.
- **Applications**:
Suitable for transporting coarse or hot materials that might damage standard conveyor belts.
- **Advantages**:
Durable and capable of handling large lumps and heavy loads.
3. **Screw Conveyors**:
- **Function**:
Used for transporting granular or small lump materials over short distances.
- **Applications**:
Commonly used in processing plants for moving materials between processes, such as from a crusher to a mill.
- **Advantages**:
Enclosed system which minimizes dust and material loss.
4. **Vibratory Conveyors**:
- **Function**:
Utilize vibration to move materials along a trough.
- **Applications**:
Often used for feeding materials into processing equipment or for separating materials by size.
- **Advantages**:
Can handle fragile materials gently and evenly distribute materials across processing equipment.
5. **Pneumatic Conveyors**:
- **Function**:
Use air pressure to transport materials through pipelines.
- **Applications**:
Typically used for fine powders or small particulate materials.
- **Advantages**:
Enclosed system that minimizes dust and contamination, suitable for handling materials over complex routes.
### Importance of Conveyors in Mineral Processing
1. **Efficiency**:
- Conveyors enable the continuous and automated transport of materials, significantly reducing manual labor and increasing the throughput of processing plants.
- They facilitate a seamless flow of materials between different stages of processing, minimizing delays and bottlenecks.
2. **Cost-effectiveness**:
- By reducing the need for trucks and other manual transport methods, conveyors help lower operational costs.
- They require less maintenance and have lower energy consumption compared to other transport methods.
3. **Safety**:
- Conveyors improve safety by reducing the need for manual material handling, thus minimizing the risk of accidents and injuries.
- Enclosed conveyor systems help control dust and prevent spillage, contributing to a cleaner and safer working environment.
4. **Flexibility and Scalability**:
- Conveyor systems can be customized to fit specific plant layouts and material characteristics.
- They can be easily expanded or modified to accommodate changes in processing requirements or increases in production capacity.
5. **Environmental Impact**:
- Conveyors help reduce the carbon footprint of mineral processing operations by minimizing the need for fuel-consuming transport vehicles.
- Enclosed systems help reduce dust emissions, contributing to better air quality and environmental compliance.
### Key Considerations in Conveyor Design
1. **Material Characteristics**:
- Understanding the properties of the material being transported (e.g., size, abrasiveness, moisture content) is crucial for selecting the appropriate conveyor type and design.
2. **Capacity and Speed**:
- The conveyor system must be designed to handle the required throughput and speed to ensure efficient processing and avoid bottlenecks.
3. **Durability and Maintenance**:
- Conveyors in mineral processing environments are subjected to harsh conditions, so materials and components must be durable and easy to maintain.
4. **Energy Efficiency**:
- Designing conveyors with energy-efficient motors and control systems can help reduce operational costs and environmental impact.
### Conclusion
Conveyors are vital for the efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness of mineral processing operations. By selecting the appropriate type and design of conveyor systems, processing plants can optimize their material handling processes, increase production capacity, and reduce operational costs.
Belt Conveyors
#### Function Belt conveyors are primarily used for transporting bulk materials over long distances in a continuous and efficient manner. They play a crucial role in the seamless flow of materials within a mineral processing plant.
#### Applications
1. **From Mine to Processing Plant**:
- Belt conveyors are used to transport raw materials from the extraction site (mine) to the processing plant, ensuring a steady supply of feedstock.
2. **Inter-plant Transport**:
- They are ideal for conveying materials between different stages of the processing plant, such as from crushers to mills, or from mills to separation units.
3. **Stockpile Handling**:
- Conveyors facilitate the movement of processed materials to storage areas or stockpiles for further processing or shipping.
#### Advantages
1. **High Efficiency**:
- Belt conveyors can transport large volumes of materials continuously over long distances with minimal downtime, enhancing overall plant efficiency.
2. **Low Operating Cost**:
- The operational cost of belt conveyors is relatively low compared to other forms of material transport, such as trucks or rail, due to lower energy consumption and reduced labor requirements.
3. **High Volume Handling**:
- They are capable of handling significant volumes of bulk materials, making them suitable for large-scale mineral processing operations.
4. **Flexibility and Versatility**:
- Belt conveyors can be designed to fit various plant layouts and can handle a wide range of materials, including ores, coal, and aggregates.
5. **Continuous Operation**:
- They enable continuous material flow without the need for frequent stops and starts, which is critical in maintaining steady production rates.
6. **Environmental Benefits**:
- Enclosed belt conveyors reduce dust and spillage, contributing to a cleaner and safer working environment and minimizing environmental impact.
### Key Design Considerations for Belt Conveyors
1. **Material Characteristics**:
- The design of the belt conveyor must consider the properties of the materials being transported, such as density, particle size, abrasiveness, and moisture content.
2. **Conveyor Length and Route**:
- The length of the conveyor and the route it takes must be carefully planned to optimize efficiency and minimize material handling time.
3. **Belt Selection**:
- Choosing the right belt type and material is essential for ensuring durability and performance, especially in harsh mining environments.
4. **Load Capacity**:
- The conveyor system must be designed to handle the maximum expected load to avoid overloading and potential failures.
5. **Energy Efficiency**:
- Incorporating energy-efficient motors and control systems can help reduce operational costs and environmental impact.
6. **Maintenance Accessibility**:
- The design should allow for easy access to components for maintenance and repairs to minimize downtime.
### Conclusion
Belt conveyors are a fundamental component in mineral processing, offering a reliable and cost-effective solution for transporting bulk materials over long distances. Their high efficiency, flexibility, and ability to handle large volumes make them indispensable in modern processing plants. Proper design and maintenance of belt conveyor systems are crucial to ensure their optimal performance and longevity.
Apron Conveyors

#### Function Apron conveyors are specifically designed to handle heavy, abrasive materials that are too challenging for standard conveyor belts. They consist of a series of overlapping metal plates (aprons) mounted on roller chains, which provide a robust and durable conveying surface.
#### Applications
1. **Transporting Coarse Materials**:
- Ideal for moving large, coarse materials such as rocks, ores, and gravel, which could potentially damage conventional belt conveyors.
2. **Handling Hot Materials**:
- Suitable for transporting materials at elevated temperatures that might cause standard conveyor belts to deteriorate, such as hot clinker, slag, or other materials exiting kilns and furnaces.
3. **Heavy Load Conveying**:
- Used for applications requiring the transport of extremely heavy loads, making them suitable for primary material handling in mining operations and processing plants.
#### Advantages
1. **Durability**:
- Apron conveyors are built to withstand the harshest conditions. The metal aprons provide a durable surface that resists wear and tear from abrasive materials.
2. **Heavy Load Capacity**:
- Capable of handling large lumps and heavy loads, making them ideal for applications that involve transporting bulky and weighty materials.
3. **Reduced Maintenance**:
- The robust construction of apron conveyors reduces the frequency and cost of maintenance compared to other conveyor types, especially in demanding environments.
4. **Versatility**:
- Can operate in both horizontal and inclined configurations, providing flexibility in plant layout and material flow design.
5. **Heat Resistance**:
- The metal construction allows apron conveyors to handle hot materials without the risk of damage, ensuring continuous operation even with high-temperature processes.
6. **Minimized Spillage**:
- The overlapping design of the aprons helps contain material spillage, maintaining a cleaner working environment and reducing material loss.
### Key Design Considerations for Apron Conveyors
1. **Material Properties**:
- The design must account for the size, weight, and abrasiveness of the materials being transported to ensure the conveyor can handle the specific requirements.
2. **Conveyor Length and Inclination**:
- Proper planning of the conveyor length and inclination angle is crucial for optimizing material flow and ensuring efficient operation.
3. **Chain Selection**:
- Selecting the appropriate roller chains that can support the load and provide smooth movement is essential for the longevity and reliability of the conveyor.
4. **Drive Systems**:
- The drive system must be powerful enough to move heavy loads over the required distances and inclines without excessive strain or wear.
5. **Wear Protection**:
- Incorporating wear-resistant materials or coatings on the aprons and other critical components can further extend the life of the conveyor.
6. **Ease of Maintenance**:
- Designing the conveyor with accessible components and modular sections can facilitate easier maintenance and reduce downtime.
### Conclusion
Apron conveyors are an essential tool in mineral processing for handling heavy, abrasive, and hot materials. Their durability, capacity to handle large loads, and resistance to wear and heat make them indispensable in environments where standard belt conveyors would fail. Proper design and maintenance are key to leveraging their full benefits and ensuring efficient, reliable material transport in harsh conditions.
Screw Conveyors
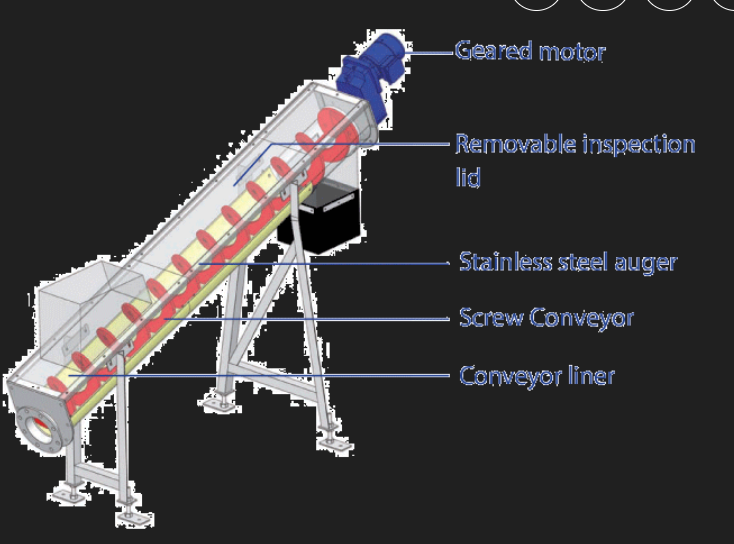
#### Function Screw conveyors are used for transporting granular or small lump materials over short distances. They consist of a helical screw blade, known as a flight, which rotates within a tube or trough, moving materials along the conveyor path.
#### Applications
1. **Inter-process Material Transport**:
- Commonly used in processing plants for moving materials between different stages of processing, such as from a crusher to a mill, or from a screening unit to a storage bin.
2. **Controlled Feeding and Discharge**:
- Ideal for controlled feeding of materials into processing equipment, ensuring a steady and consistent flow of material.
3. **Mixing and Blending**:
- In some applications, screw conveyors can also perform mixing or blending of materials as they convey, particularly useful in chemical processing.
4. **Handling Semi-solid Materials**:
- Suitable for transporting semi-solid materials, such as sludge or wet ore concentrates, which might be difficult to handle with other types of conveyors.
#### Advantages
1. **Enclosed System**:
- The enclosed design minimizes dust and material loss, contributing to a cleaner and safer working environment.
2. **Compact and Versatile**: - Screw conveyors can be installed in confined spaces and customized to fit specific process requirements, providing versatility in plant design.
3. **Ease of Maintenance**:
- With fewer moving parts compared to other conveyor systems, screw conveyors are relatively easy to maintain and have lower maintenance costs.
4. **Flexibility**:
- Can be designed to handle a variety of materials, from fine powders to small lumps, making them adaptable to different processing needs.
5. **Energy Efficiency**:
- They consume less energy compared to other types of conveyors, especially for short-distance transport.
### Key Design Considerations for Screw Conveyors
1. **Material Characteristics**:
- The design should consider the properties of the materials being transported, such as bulk density, particle size, abrasiveness, and moisture content.
2. **Conveyor Length and Slope**:
- Screw conveyors are best suited for short distances. The length and slope should be optimized to ensure efficient material transport and prevent material backflow.
3. **Flight Design**:
- The flight design (e.g., pitch, thickness, and shape) should be tailored to the specific material and application to ensure efficient transport and minimize wear.
4. **Tubular vs. Trough Design**:
- Choosing between a tubular or trough design depends on the material and application. Tubular designs offer better containment, while trough designs can be easier to access for cleaning and maintenance.
5. **Drive Mechanism**:
- The drive system must be powerful enough to handle the required load and torque, ensuring smooth and reliable operation.
6. **Wear and Corrosion Resistance**:
- Using wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials for the screw and housing can extend the life of the conveyor, especially when handling abrasive or corrosive materials.
### Conclusion
Screw conveyors are a vital component in mineral processing for the efficient transport of granular and small lump materials over short distances. Their enclosed design minimizes dust and material loss, contributing to a cleaner and safer work environment.
Their versatility, ease of maintenance, and energy efficiency make them an excellent choice for various applications within processing plants. Proper design and customization are essential to maximize their benefits and ensure reliable operation.
Vibratory Conveyors
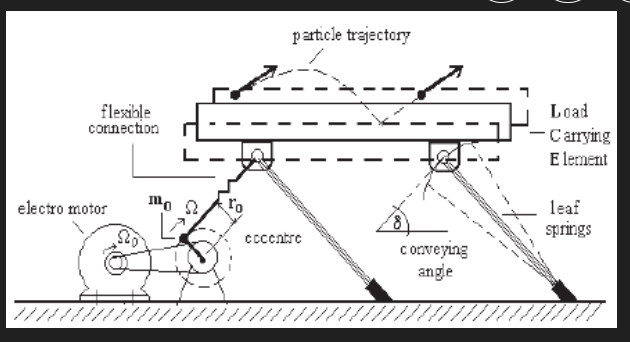
#### Function Vibratory conveyors utilize vibration to move materials along a trough or bed. The vibrating motion, generated by electromagnetic, mechanical, or hydraulic systems, propels materials forward in a controlled manner.
#### Applications
1. **Feeding Processing Equipment**:
- Often used to feed materials into processing equipment such as crushers, screens, or mills. The controlled flow ensures that the equipment operates efficiently without overloading.
2. **Material Separation**:
- Suitable for separating materials by size through vibratory screening processes, where different-sized particles are sorted and directed to different downstream processes.
3. **Even Distribution**:
- Effective in evenly distributing materials across the width of processing equipment, such as evenly spreading materials across a screen deck or feeding material uniformly into a kiln or furnace.
4. **Cooling and Drying**:
- Can be used in processes where materials need to be cooled or dried as they are transported. Vibratory conveyors with perforated troughs allow air to flow through the material, facilitating these processes.
5. **Handling Fragile Materials**:
- Ideal for handling fragile or delicate materials that could be damaged by more aggressive conveying methods, such as fine powders, seeds, or processed food items.
#### Advantages
1. **Gentle Handling**:
- The vibratory motion can be finely controlled to handle fragile materials gently, minimizing the risk of damage during transport.
2. **Even Material Distribution**:
- Ensures uniform distribution of materials across processing equipment, improving efficiency and product quality.
3. **Flexibility**:
- Can be designed to handle a wide range of materials and can be easily adjusted to accommodate different process requirements.
4. **Low Maintenance**:
- With fewer moving parts than some other conveyor types, vibratory conveyors typically require less maintenance and have lower operational costs.
5. **Clean Operation**:
- Enclosed or partially enclosed designs help minimize dust generation and spillage, contributing to a cleaner work environment.
6. **Energy Efficiency**:
- Vibratory conveyors are energy-efficient, especially for short to medium-distance transport, and can be designed to use minimal power while maintaining high throughput.
### Key Design Considerations for Vibratory Conveyors
1. **Material Properties**:
- The design must account for the characteristics of the material being conveyed, such as particle size, bulk density, and moisture content, to ensure efficient transport.
2. **Amplitude and Frequency**:
- The amplitude (height) and frequency (speed) of the vibrations need to be carefully controlled to achieve the desired material flow and handling characteristics.
3. **Trough Design**:
- The trough can be open, partially enclosed, or fully enclosed, depending on the application and the need to control dust or contain the material.
4. **Drive Mechanism**:
- Choosing the appropriate drive mechanism (electromagnetic, mechanical, or hydraulic) is crucial for ensuring the conveyor operates efficiently and reliably.
5. **Wear Resistance**:
- Using wear-resistant materials for the trough and other critical components can extend the life of the conveyor, particularly when handling abrasive materials.
6. **Integration with Processing Equipment**:
- The conveyor must be designed to integrate seamlessly with other processing equipment, ensuring a smooth flow of materials and optimizing overall process efficiency.
### Conclusion
Vibratory conveyors are an essential tool in mineral processing, offering a versatile and efficient solution for transporting and handling a wide range of materials. Their ability to gently handle fragile materials, evenly distribute materials, and operate with low maintenance makes them invaluable in various applications. Proper design and customization are key to maximizing their benefits and ensuring reliable operation within processing plants.
Pneumatic Conveyors
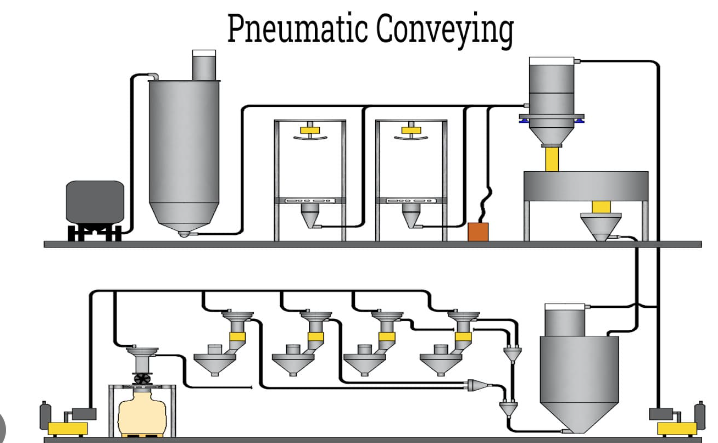
#### Function Pneumatic conveyors use air pressure or vacuum to transport materials through pipelines. They rely on the flow of air or another gas to move bulk materials, typically fine powders or small particulate materials, through enclosed tubes or ducts.
#### Applications
1. **Transporting Fine Powders**:
- Commonly used to convey fine powders such as cement, fly ash, or mineral dust from one part of a processing plant to another.
2. **Handling Small Particulate Materials**:
- Suitable for materials like grains, plastic pellets, and small granular products, often used in industries such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, and chemical manufacturing.
3. **Complex Routing**:
- Effective for moving materials over complex routes within a plant, including vertical and horizontal pathways, as well as around obstacles.
4. **Feeding Processing Equipment**:
- Used to feed materials into processing equipment like mixers, hoppers, or reactors with precise control over the material flow.
5. **Bulk Material Handling**:
- Employed in bulk material handling systems where materials need to be transferred from storage silos to various processing units.
#### Advantages
1. **Enclosed System**:
- The fully enclosed nature of pneumatic conveyors minimizes dust generation and material contamination, leading to a cleaner and safer working environment.
2. **Flexibility in Routing**:
- Capable of transporting materials over long distances and through complex routes, including vertical lifts, tight bends, and horizontal spans, providing flexibility in plant layout.
3. **Reduced Material Degradation**:
- The gentle handling of materials reduces the risk of degradation, which is particularly important for fragile or sensitive materials.
4. **Minimal Maintenance**:
- Fewer moving parts compared to mechanical conveyors result in lower maintenance requirements and reduced downtime.
5. **High Throughput**:
- Can transport large volumes of material quickly, improving the efficiency of material handling operations.
6. **Safety**: - Reduces the risk of dust explosions, particularly when handling combustible powders, by minimizing dust accumulation and using inert gases if necessary.
### Key Design Considerations for Pneumatic Conveyors
1. **Material Properties**:
- Understanding the properties of the material, such as particle size, density, abrasiveness, and moisture content, is crucial for designing an efficient pneumatic conveying system.
2. **System Design (Pressure vs. Vacuum)**:
- Deciding between a pressure system (pushing materials) and a vacuum system (pulling materials) depends on the specific application and material characteristics.
3. **Pipeline Layout**:
- The layout of the pipelines, including the length, diameter, and number of bends, affects the system's efficiency and must be optimized to minimize pressure drops and material degradation.
4. **Air Supply and Filtration**:
- Ensuring a consistent and clean air supply is critical for system performance. Adequate filtration is necessary to prevent contaminants from entering the system and affecting the material.
5. **Control Systems**:
- Advanced control systems can help monitor and regulate the flow of materials, ensuring consistent and efficient operation.
6. **Wear and Abrasion Resistance**:
- Using wear-resistant materials for pipelines and components is essential when handling abrasive materials to extend the system's lifespan.
### Conclusion
Pneumatic conveyors are a vital component in mineral processing and various other industries, providing a flexible, efficient, and clean method of transporting fine powders and small particulate materials.
Their enclosed design minimizes dust and contamination, while their ability to handle complex routing and long distances enhances plant layout flexibility. Proper design and understanding of material characteristics are key to maximizing the benefits of pneumatic conveying systems and ensuring reliable and efficient operation.
Efficiency of Conveyors in Mineral Processing
#### Continuous and Automated Transport
1. **Reduction of Manual Labor**:
- **Automated Systems**:
Conveyors automate the transport of materials, eliminating the need for manual handling and reducing labor costs and physical strain on workers.
- **Consistency**:
Automation ensures a consistent flow of materials, which is crucial for maintaining steady production rates.
2. **Increased Throughput**:
- **High Capacity**:
Conveyors are designed to handle large volumes of materials continuously, increasing the overall throughput of processing plants.
- **Speed and Efficiency**:
Materials are moved quickly and efficiently from one stage to another, enhancing productivity.
#### Seamless Flow of Materials
1. **Minimization of Delays and Bottlenecks**:
- **Continuous Operation**:
Conveyors provide a continuous flow of materials, reducing the likelihood of delays that can occur with batch processing or manual transport methods.
- **Improved Coordination**:
By synchronizing the transport of materials between different stages, conveyors help in maintaining a smooth and coordinated workflow, preventing bottlenecks.
2. **Optimized Plant Layout**:
- **Flexible Routing**:
Conveyors can be designed to navigate complex plant layouts, ensuring that materials are delivered exactly where they are needed, when they are needed.
- **Efficient Use of Space**:
The flexibility in conveyor design allows for the optimal use of available space, enabling more efficient plant layouts and better utilization of resources.
#### Additional Benefits
1. **Enhanced Safety**:
- **Reduced Handling Risks**: By minimizing the need for manual handling, conveyors reduce the risk of injuries and accidents associated with lifting and moving heavy materials.
- **Enclosed Systems**:
Many conveyors are designed with enclosures to prevent spillage and contain dust, contributing to a safer and cleaner work environment.
2. **Cost-effectiveness**:
- **Lower Operational Costs**:
Automated conveyor systems have lower operational costs compared to manual transport methods or vehicles like trucks and forklifts.
- **Energy Efficiency**:
Modern conveyor systems are designed to be energy-efficient, further reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
3. **Reliability and Durability**:
- **Long Service Life**:
Conveyors are built to withstand the harsh conditions of mineral processing environments, offering reliable performance and long service life.
- **Low Maintenance**:
With fewer moving parts and robust construction, conveyors typically require less maintenance compared to other transport methods, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
### Conclusion
Conveyors significantly enhance the efficiency of mineral processing operations by enabling continuous and automated material transport, reducing manual labor, and increasing throughput.
Their ability to facilitate a seamless flow of materials between different stages of processing minimizes delays and bottlenecks, optimizing overall plant performance. In addition to these efficiency gains, conveyors also offer benefits in terms of safety, cost-effectiveness, and reliability, making them a crucial component in modern mineral processing plants.
Cost-effectiveness of Conveyors in Mineral Processing
### Cost-effectiveness of Conveyors in Mineral Processing
#### Reduction of Operational Costs
1. **Minimized Need for Trucks and Manual Transport**:
- **Reduced Labor Costs**:
By automating material transport, conveyors significantly lower the need for manual labor, thus reducing labor costs.
- **Lower Fuel Costs**:
Conveyors eliminate the reliance on trucks and other fuel-consuming vehicles, leading to substantial savings on fuel expenses.
- **Decreased Vehicle Maintenance**:
With fewer trucks in operation, maintenance costs for these vehicles are reduced, including savings on parts, repairs, and downtime.
2. **Lower Energy Consumption**:
- **Energy-efficient Motors**:
Modern conveyor systems are equipped with energy-efficient motors and variable frequency drives, reducing overall energy consumption.
- **Continuous Operation**:
Unlike vehicles that consume more fuel during starts and stops, conveyors operate continuously and more efficiently, leading to energy savings.
#### Reduced Maintenance Costs
1. **Fewer Moving Parts**:
- **Simpler Mechanisms**:
Conveyors have fewer moving parts compared to trucks and other transport vehicles, which means there are fewer components that can wear out or fail.
- **Less Frequent Repairs**:
The simplicity and robustness of conveyor systems result in fewer breakdowns and lower repair frequencies.
2. **Durable Construction**:
- **High-quality Materials**:
Conveyors are built with durable materials designed to withstand harsh processing environments, which reduces wear and tear.
- **Extended Lifespan**:
The longevity of conveyor systems means less frequent replacements and lower long-term capital expenditures.
3. **Lower Maintenance Requirements**:
- **Routine Maintenance**:
Conveyor systems typically require less intensive and less frequent maintenance compared to vehicles, which translates to lower maintenance costs.
- **Predictive Maintenance**:
Many modern conveyor systems are equipped with sensors and monitoring systems that enable predictive maintenance, identifying potential issues before they lead to costly failures.
#### Additional Economic Benefits
1. **Increased Productivity**:
- **Continuous Material Flow**:
Conveyors ensure a continuous and steady flow of materials, enhancing overall plant productivity and efficiency.
- **Reduced Downtime**:
Automated and reliable conveyor systems reduce downtime associated with manual transport methods and vehicle breakdowns.
2. **Enhanced Safety and Compliance**:
- **Reduced Accidents**:
By minimizing manual handling and vehicle operation, conveyors lower the risk of workplace accidents, which can result in cost savings from fewer injury-related expenses.
- **Environmental Compliance**:
Reduced fuel consumption and dust generation help plants meet environmental regulations, potentially avoiding fines and enhancing sustainability efforts.
3. **Optimized Space Utilization**:
- **Efficient Layouts**:
Conveyors can be integrated into plant layouts to optimize space utilization, reducing the need for extensive infrastructure and lowering construction costs.
- **Scalability**:
Conveyor systems can be easily expanded or reconfigured to meet changing production needs, providing cost-effective scalability.
### Conclusion
Conveyors are a cost-effective solution for material transport in mineral processing, providing significant savings in operational costs by reducing reliance on trucks and manual labor. Their lower energy consumption, reduced maintenance needs, and durable construction contribute to ongoing cost savings. Additionally, conveyors enhance productivity, safety, and space utilization, making them a financially prudent investment for mineral processing plants.
Safety Benefits of Conveyors in Mineral Processing
#### Reduction in Manual Material Handling
1. **Minimization of Accidents and Injuries**:
- **Decreased Physical Strain**:
Automating the transport of materials reduces the need for manual lifting, carrying, and moving of heavy or bulky items, which lowers the risk of musculoskeletal injuries among workers.
- **Fewer Handling Errors**:
Automated conveyors eliminate many of the errors and mishaps associated with manual material handling, such as dropping or improperly stacking materials, which can lead to accidents.
2. **Improved Ergonomics**:
- **Ergonomic Design**:
Conveyors can be designed at optimal heights and configurations to facilitate better ergonomic conditions for workers, reducing strain and injury risks associated with repetitive manual tasks.
- **Consistent Operation**:
The consistent and predictable operation of conveyors minimizes sudden movements and manual adjustments, further enhancing worker safety.
#### Enclosed Systems for Dust Control and Spill Prevention
1. **Dust Control**:
- **Reduced Airborne Particles**:
Enclosed conveyor systems contain dust within the system, preventing it from becoming airborne and improving air quality in the working environment.
- **Health Protection**:
Lower levels of airborne dust reduce the risk of respiratory issues and long-term health problems for workers, contributing to a healthier workplace.
2. **Spillage Prevention**:
- **Containment**:
Enclosed conveyors prevent materials from spilling onto the floor, which can create slip and trip hazards. This containment ensures a cleaner and safer working environment.
- **Efficient Cleanup**:
Enclosed systems make it easier to clean up any potential spills, reducing the time and labor required for maintenance and minimizing disruptions to operations.
#### Additional Safety Advantages
1. **Safe Equipment Operation**:
- **Automated Controls**:
Modern conveyor systems are equipped with advanced safety features, such as emergency stop buttons, sensors, and automated shutoff mechanisms, which enhance operational safety.
- **Predictive Maintenance**:
Integrated monitoring systems can detect potential issues early, allowing for proactive maintenance and reducing the risk of sudden failures that could pose safety hazards.
2. **Reduced Vehicle Traffic**:
- **Less Internal Traffic**:
By reducing the need for forklifts and trucks within the plant, conveyors decrease the potential for collisions and accidents associated with vehicle traffic.
- **Improved Workflow**:
The elimination of frequent vehicle movement creates a more organized and safer working environment, reducing the risk of accidents involving workers and machinery.
3. **Enhanced Fire Safety**:
- **Fire-resistant Materials**:
Conveyor systems can be constructed from fire-resistant materials and designed to prevent the accumulation of combustible dust, reducing fire hazards.
- **Isolation Zones**:
Conveyors can be equipped with isolation zones and fire suppression systems to contain and mitigate the spread of fire in the event of an incident.
4. **Compliance with Safety Regulations**:
- **Regulatory Adherence**:
Using conveyors helps facilities comply with occupational health and safety regulations by reducing manual handling and controlling dust, which can prevent costly fines and improve overall safety standards.
- **Worker Training**:
Implementing conveyor systems often includes comprehensive training programs for operators, further promoting a culture of safety and awareness.
### Conclusion
Conveyors significantly enhance safety in mineral processing plants by reducing the need for manual material handling and minimizing the risk of accidents and injuries.
Enclosed conveyor systems effectively control dust and prevent spillage, contributing to a cleaner and safer working environment. The additional safety features and regulatory compliance associated with conveyors further bolster their role in creating a secure and efficient workplace.
Flexibility and Scalability of Conveyor Systems in Mineral Processing
#### Customization to Fit Specific Plant Layouts and Material Characteristics
1. **Tailored Design**:
- **Custom Configurations**: Conveyor systems can be designed to match the unique layout of a processing plant, navigating around existing structures and equipment.
- **Material-Specific Features**:
Conveyors can be customized based on the properties of the materials being transported, such as bulk density, particle size, abrasiveness, and moisture content.
For example, belt materials, trough designs, and drive mechanisms can be selected to best handle specific materials.
2. **Versatile Routing**:
- **Horizontal and Vertical Transport**:
Conveyors can be configured to move materials horizontally, vertically, or at an incline, making it possible to transport materials between different levels of a plant.
- **Complex Pathways**:
They can be designed to follow complex pathways, including curves and bends, which allows for optimal use of space and seamless integration into existing plant infrastructure.
#### Easy Expansion and Modification
1. **Scalable Systems**:
- **Modular Components**:
Many conveyor systems use modular components that can be easily added or rearranged. This modularity makes it straightforward to extend the length of a conveyor or add additional sections as production needs grow.
- **Adaptable Framework**:
The framework of conveyor systems can be adjusted to accommodate new processing equipment or changes in plant layout without requiring significant structural modifications.
2. **Flexible Adaptation**:
- **Process Changes**:
Conveyor systems can be reconfigured to adapt to changes in processing requirements, such as new material types or changes in production processes. This adaptability ensures that the conveyor system remains efficient and effective even as processing needs evolve.
- **Increased Capacity**:
As production capacity increases, conveyor systems can be upgraded with more powerful drives, wider belts, or additional lines to handle higher volumes of material.
#### Additional Benefits
1. **Cost-Effective Upgrades**:
- **Incremental Investment**:
The ability to expand and modify conveyor systems incrementally allows plants to scale up operations without the need for large upfront capital expenditures.
- **Reduced Downtime**:
Modular and flexible designs mean that expansions and modifications can often be carried out with minimal disruption to ongoing operations, reducing downtime and associated costs.
2. **Integration with Advanced Technologies**:
- **Automation and Control**:
Conveyor systems can be integrated with advanced automation and control technologies, such as sensors and automated sorting systems, to enhance efficiency and adapt to new processing technologies.
- **Smart Conveyors**:
Implementing smart conveyor systems with real-time monitoring and control capabilities enables better handling of variable production demands and material characteristics.
3. **Future-Proofing**:
- **Long-Term Viability**:
Investing in flexible and scalable conveyor systems ensures that a processing plant can continue to meet future production goals and adapt to market changes without needing to overhaul the entire material handling infrastructure.
- **Sustainability**:
Flexible systems can be designed to incorporate sustainable practices, such as energy-efficient motors and recyclable materials, supporting long-term environmental goals.
### Conclusion
Conveyor systems offer exceptional flexibility and scalability for mineral processing operations.
Their ability to be customized to specific plant layouts and material characteristics ensures efficient and effective material handling. The ease with which they can be expanded or modified allows plants to adapt to changes in processing requirements and increases in production capacity without significant disruptions or costs.
This adaptability makes conveyors a valuable long-term investment for any processing plant looking to maintain efficiency and competitiveness in a dynamic industry.
Environmental Impact of Conveyors in Mineral Processing
#### Reduction in Carbon Footprint
1. **Minimized Use of Fuel-Consuming Vehicles**:
- **Lower Fuel Consumption**:
By replacing trucks and other fuel-consuming transport vehicles, conveyors reduce the overall fuel consumption of mineral processing operations. This reduction in fuel use directly translates to lower carbon emissions.
- **Reduced Vehicle Emissions**:
Fewer transport vehicles mean reduced emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter (PM), all of which contribute to air pollution and climate change.
2. **Energy Efficiency**:
- **Efficient Electric Motors**:
Modern conveyor systems are powered by energy-efficient electric motors, which consume less energy compared to the internal combustion engines of transport vehicles.
- **Variable Speed Drives**:
The use of variable frequency drives (VFDs) allows conveyors to operate at optimal speeds, further reducing energy consumption and enhancing overall energy efficiency.
#### Reduction in Dust Emissions
1. **Enclosed Conveyor Systems**:
- **Dust Containment**:
Enclosed conveyor systems are designed to contain dust within the system, preventing it from becoming airborne and reducing dust pollution.
- **Improved Air Quality**:
By minimizing dust emissions, enclosed conveyors contribute to better air quality within the processing plant and its surrounding environment, benefiting both workers and nearby communities.
2. **Compliance with Environmental Regulations**:
- **Regulatory Adherence**:
Reducing dust emissions helps processing plants comply with environmental regulations and standards, avoiding fines and penalties associated with non-compliance.
- **Sustainable Practices**:
Adopting enclosed conveyor systems as part of a broader strategy for dust control supports the industry's move towards more sustainable and environmentally responsible practices.
#### Additional Environmental Benefits
1. **Reduced Noise Pollution**:
- **Quieter Operation**:
Conveyor systems generally produce less noise compared to the operation of trucks and heavy vehicles, contributing to lower noise pollution in and around the processing plant.
- **Enhanced Worker Health**:
Lower noise levels improve working conditions and reduce the risk of hearing damage among plant workers.
2. **Less Land Disturbance**:
- **Compact Footprint**:
Conveyor systems, especially those that are elevated or designed to follow the contours of the land, require less ground disturbance compared to the construction and maintenance of roads and pathways for trucks.
- **Preservation of Ecosystems**:
Reduced land disturbance helps preserve local ecosystems and minimizes the impact on wildlife habitats.
3. **Waste Reduction**:
- **Efficient Material Handling**:
Conveyors facilitate more precise and efficient handling of materials, reducing spillage and waste. This efficiency not only conserves resources but also minimizes the environmental impact of waste disposal.
- **Recycling and Reusability**:
Many components of conveyor systems are recyclable or can be reused, reducing the environmental footprint associated with the disposal of equipment.
4. **Support for Renewable Energy Integration**:
- **Renewable Energy Sources**:
Conveyor systems can be integrated with renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, further reducing their environmental impact and supporting the transition to sustainable energy practices.
### Conclusion
Conveyor systems play a significant role in reducing the environmental impact of mineral processing operations. By minimizing the need for fuel-consuming transport vehicles, they help lower the carbon footprint and reduce emissions. Enclosed conveyor systems effectively control dust, contributing to better air quality and environmental compliance.
Additional benefits, such as reduced noise pollution, less land disturbance, and efficient material handling, further enhance their environmental advantages. Adopting conveyor systems supports the industry's move towards more sustainable and environmentally responsible practices, making them a key component in modern mineral processing operations.
Key Considerations in Conveyor Design for Mineral Processing
#### Material Characteristics
1. **Size and Shape**:
- **Particle Size**:
The size of the materials being transported affects the choice of conveyor. Larger particles may require wider belts or more robust systems like apron conveyors, while fine particles might be best suited for pneumatic or screw conveyors.
- **Shape and Uniformity**:
Irregularly shaped materials may need specialized handling systems to prevent blockages and ensure smooth transport.
2. **Abrasiveness**:
- **Wear Resistance**:
Materials with high abrasiveness require conveyors with wear-resistant components, such as reinforced belts or hardened steel parts, to withstand the constant friction and extend the system’s lifespan.
- **Lining and Coating**:
Protective linings or coatings can be applied to reduce wear and tear on conveyor surfaces.
3. **Moisture Content**:
- **Handling Wet Materials**:
Wet or sticky materials may require conveyors with special cleaning mechanisms to prevent buildup and ensure consistent flow.
- **Corrosion Resistance**:
Materials with high moisture content can lead to corrosion; therefore, using corrosion-resistant materials and coatings is essential.
4. **Bulk Density**:
- **Load Capacity**:
Understanding the bulk density of the material is crucial for determining the load capacity and structural requirements of the conveyor system.
#### Capacity and Speed
1. **Throughput Requirements**:
- **Design Capacity**:
The conveyor must be capable of handling the maximum expected throughput to avoid bottlenecks. This includes considering peak load scenarios.
- **Scalability**:
The system should be scalable to accommodate future increases in production capacity.
2. **Conveyor Speed**:
- **Optimal Speed**:
Balancing speed and capacity is essential to ensure efficient material handling without causing spillage or system strain.
- **Adjustable Speed**:
Implementing variable speed drives can help optimize the conveyor’s performance based on changing operational demands.
#### Durability and Maintenance
1. **Robust Construction**:
- **Material Selection**:
Using high-quality, durable materials in the construction of conveyors helps withstand the harsh conditions of mineral processing environments.
- **Component Strength**:
Components such as belts, chains, rollers, and bearings should be selected based on their ability to handle heavy loads and resist wear.
2. **Ease of Maintenance**:
- **Accessibility**:
Designing conveyors with easy access points for inspection and maintenance tasks can significantly reduce downtime.
- **Modular Design**:
Modular components allow for quick replacements and repairs, minimizing operational interruptions.
3. **Preventive Maintenance**:
- **Monitoring Systems**:
Incorporating sensors and monitoring systems can help detect issues early and schedule maintenance before major failures occur.
- **Maintenance Planning**: Establishing a proactive maintenance schedule based on the specific wear and tear patterns of the conveyor system.
#### Energy Efficiency
1. **Efficient Motors**:
- **High-Efficiency Motors**:
Using energy-efficient motors can significantly reduce the operational costs and environmental impact of the conveyor system.
- **Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs)**:
Implementing VFDs allows for precise control of motor speed and energy consumption, optimizing performance under varying load conditions.
2. **Power Consumption**:
- **Load Management**:
Designing the conveyor system to operate efficiently under different load conditions helps reduce unnecessary power consumption.
- **Energy Recovery Systems**:
Implementing energy recovery technologies, such as regenerative drives, can help capture and reuse energy, further enhancing efficiency.
3. **System Optimization**:
- **Design Layout**:
Optimizing the layout of the conveyor system to minimize unnecessary travel distances and elevation changes can reduce energy usage.
- **Smart Controls**:
Integrating advanced control systems that adjust the conveyor operation based on real-time data and demand can lead to significant energy savings.
### Conclusion
Designing an efficient and effective conveyor system for mineral processing involves careful consideration of material characteristics, capacity and speed requirements, durability, maintenance, and energy efficiency.
By understanding the specific properties of the materials being transported and the operational demands of the processing plant, designers can select and customize conveyor systems that enhance productivity, reduce operational costs, and minimize environmental impact. Implementing robust construction, preventive maintenance practices, and energy-efficient technologies ensures long-term reliability and sustainability of the conveyor system.
Conveyor Belt Installation in Mineral Processing
#### Pre-Installation Preparation
1. **Site Survey and Planning**:
- **Site Inspection**:
Conduct a thorough site inspection to assess the installation area and identify any potential obstacles or hazards.
- **Layout Design**:
Develop a detailed layout plan, including the conveyor path, support structures, and integration with existing systems.
- **Permits and Approvals**:
Obtain all necessary permits and approvals from regulatory bodies and ensure compliance with local safety and environmental regulations.
2. **Material and Equipment Preparation**:
- **Conveyor Components**: Ensure all conveyor components (belts, pulleys, idlers, motors, etc.) are on-site and meet the required specifications.
- **Tools and Equipment**:
Gather all necessary tools and equipment, including wrenches, clamps, measuring tapes, and safety gear.
3. **Safety Measures**:
- **Safety Plan**:
Develop a comprehensive safety plan, including risk assessments, emergency procedures, and safety protocols.
- **Training**:
Provide safety training to all personnel involved in the installation process.
#### Installation Process
1. **Foundation and Structure Installation**:
- **Support Structures**:
Erect the support structures, such as frames and brackets, ensuring they are level and securely anchored to the foundation.
- **Alignment**:
Verify the alignment of the support structures to ensure the conveyor will run straight and true.
2. **Installing the Conveyor Belt**:
- **Positioning the Belt**:
Place the conveyor belt along the path of the conveyor structure. Use a crane or other lifting devices if necessary to handle heavy or long sections of the belt.
- **Joining the Belt**:
If the belt is supplied in sections, join the sections together using mechanical fasteners or vulcanization, depending on the belt type and specifications.
- **Tensioning the Belt**:
Gradually tension the belt to the manufacturer’s recommended tension. This may involve adjusting tensioners, take-up units, or screw-type adjustments.
3. **Installing Conveyor Components**:
- **Pulleys and Idlers**: Install the pulleys (drive, tail, and bend) and idlers along the conveyor path. Ensure they are aligned correctly to prevent belt misalignment.
- **Drive System**:
Install the drive system, including the motor, gearbox, and drive pulley. Ensure all components are securely mounted and aligned.
- **Tracking Devices**:
Install any tracking devices or sensors designed to monitor and correct belt alignment during operation.
4. **Electrical and Control Systems**:
- **Wiring and Connections**:
Connect the electrical components, including the motor, control panels, and safety switches, following electrical codes and manufacturer instructions.
- **Control Systems**:
Install and configure the control systems, such as start/stop buttons, speed controllers, and emergency stop mechanisms.
#### Post-Installation Procedures
1. **Inspection and Testing**:
- **Initial Inspection**:
Conduct a thorough inspection of the entire conveyor system to ensure all components are properly installed and secured.
- **Test Run**:
Perform a test run of the conveyor system to check for proper operation, alignment, and tension. Monitor for any unusual noises, vibrations, or signs of misalignment.
2. **Adjustments and Fine-Tuning**:
- **Alignment Adjustments**: Make any necessary adjustments to the alignment of the belt, pulleys, and idlers to ensure smooth and efficient operation.
- **Tension Adjustments**:
Fine-tune the belt tension to achieve optimal performance and prevent slippage or excessive wear.
3. **Safety Checks**:
- **Safety Devices**:
Verify that all safety devices, such as emergency stops and guards, are functioning correctly and are accessible.
- **Training and Signage**:
Ensure that all personnel are trained in the operation and safety features of the conveyor system, and install appropriate warning signs and labels.
#### Maintenance and Monitoring
1. **Routine Maintenance**:
- **Regular Inspections**:
Schedule regular inspections to check for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment.
- **Lubrication**:
Keep all moving parts properly lubricated to reduce friction and wear.
- **Belt Cleaning**:
Regularly clean the belt to prevent buildup of material, which can cause misalignment and damage.
2. **Monitoring Systems**:
- **Sensors and Alarms**:
Utilize sensors and alarms to continuously monitor the conveyor system’s performance and detect any potential issues early.
- **Data Analysis**:
Analyze operational data to identify trends and predict maintenance needs, helping to prevent unexpected downtime.
### Conclusion
Proper installation of a conveyor belt in a mineral processing environment is essential for ensuring efficient and reliable operation.
By following a detailed and systematic approach, from pre-installation preparation through to post-installation procedures, and maintaining rigorous safety standards, you can achieve a successful installation that minimizes downtime and enhances productivity. Regular maintenance and monitoring further ensure the longevity and optimal performance of the conveyor system.
Belt Tracking & Conveyor Maintenance in Mineral Processing
#### Belt Tracking Belt tracking is the process of ensuring that the conveyor belt runs straight and true along the conveyor system. Proper belt tracking is essential to prevent damage, reduce wear, and maintain efficiency.
1. **Causes of Belt Misalignment**:
- **Incorrectly Installed Components**: Misalignment of pulleys, idlers, or rollers.
- **Uneven Loading**:
Uneven distribution of material on the belt can cause the belt to shift to one side.
- **Worn or Damaged Components**:
Wear and tear on conveyor components, such as idlers or rollers, can lead to misalignment.
- **Belt Tension**:
Incorrect tension can cause the belt to drift off-center.
2. **Methods for Tracking Conveyor Belts**:
- **Initial Alignment**:
Ensure all conveyor components are aligned correctly during installation.
- **Adjusting Idlers and Rollers**:
Use adjustable idlers and rollers to guide the belt back into proper alignment. Adjust these components incrementally and evenly on both sides of the belt.
- **Belt Tensioning**:
Properly tension the belt to avoid sagging or excessive tightness. Use tensioners or take-up units to adjust the tension as needed.
- **Training Idlers**:
Install training idlers that automatically guide the belt back into alignment. These idlers pivot or tilt to correct the belt's path.
- **Regular Inspection**:
Regularly inspect the belt and conveyor components for signs of misalignment, wear, or damage. Promptly address any issues found.
#### Conveyor Maintenance Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the conveyor system operates efficiently, safely, and with minimal downtime.
1. **Preventive Maintenance**:
- **Scheduled Inspections**:
Develop a maintenance schedule for routine inspections of the conveyor system. Inspect all components, including belts, pulleys, idlers, rollers, bearings, and drive systems.
- **Lubrication**:
Regularly lubricate moving parts, such as bearings and rollers, to reduce friction and wear.
- **Belt Cleaning**:
Keep the conveyor belt clean to prevent material buildup, which can lead to misalignment and damage. Use belt scrapers, brushes, or wash systems.
- **Component Replacement**:
Replace worn or damaged components promptly to prevent further damage and ensure smooth operation.
2. **Condition Monitoring**:
- **Sensors and Alarms**:
Install sensors to monitor belt tension, alignment, temperature, and other critical parameters. Use alarms to alert operators to potential issues.
- **Data Analysis**:
Analyze operational data to identify patterns and predict maintenance needs, helping to prevent unexpected failures.
3. **Common Maintenance Tasks**:
- **Belt Inspection**:
Regularly inspect the belt for signs of wear, damage, or fraying. Look for tears, cuts, or abrasions that may require repair or replacement.
- **Pulley and Idler Inspection**:
Check pulleys and idlers for alignment, wear, and proper rotation. Replace any that show signs of excessive wear or damage.
- **Drive System Maintenance**:
Inspect the drive motor, gearbox, and drive belt or chain. Ensure all components are functioning correctly and are properly lubricated.
- **Frame and Structure Check**:
Inspect the conveyor frame and support structures for any signs of damage, corrosion, or misalignment. Make necessary repairs or adjustments.
4. **Safety Protocols**:
- **Lockout/Tagout**:
Implement lockout/tagout procedures during maintenance to ensure the conveyor system is safely de-energized and cannot be accidentally started.
- **Safety Training**:
Provide training for maintenance personnel on safe work practices, proper use of tools and equipment, and emergency procedures.
### Conclusion
Effective belt tracking and regular conveyor maintenance are crucial for the efficient and safe operation of conveyor systems in mineral processing environments. Proper belt tracking prevents misalignment, reduces wear, and enhances the system's overall performance.
Implementing a comprehensive maintenance program that includes preventive maintenance, condition monitoring, and adherence to safety protocols ensures the longevity and reliability of the conveyor system. By addressing potential issues early and maintaining all components in good working condition, operators can minimize downtime, reduce operational costs, and maintain a high level of productivity.
Common Causes of Belt Misalignment
#### 1. Improper Installation
- **Misaligned Components**:
Incorrect alignment of pulleys, idlers, or rollers during installation can cause the belt to run off-center.
- **Frame Misalignment**:
If the conveyor frame is not straight or level, it can lead to belt tracking issues. #### 2. Uneven Loading
- **Asymmetric Load Distribution**: Uneven loading of material onto the conveyor belt can cause it to shift to one side. This can happen if material is fed unevenly or if the loading chute is off-center.
- **Impact Loading**:
Heavy, uneven impact of material on the belt can create temporary misalignment.
#### 3. Worn or Damaged Components
- **Worn Idlers and Rollers**:
Idlers and rollers that are worn or damaged can create uneven surfaces, causing the belt to wander.
- **Damaged Belts**:
Tears, frayed edges, or other damage to the belt itself can cause it to track improperly.
#### 4. Belt Tension Issues -
**Incorrect Tension**:
Belts that are either too loose or too tight can cause misalignment. Loose belts can sag and wander, while overly tight belts can cause excessive strain on the components.
- **Uneven Tension**:
Uneven tension across the width of the belt can cause one side to be tighter than the other, leading to tracking problems.
#### 5. Material Build-Up
- **Carryback**:
Material that sticks to the belt and is not properly removed can accumulate on pulleys and idlers, causing misalignment.
- **Spillage**:
Material that spills over the sides of the belt can accumulate on the conveyor structure and cause tracking issues.
#### 6. Misaligned Pulleys and Idlers
- **Skewed Pulleys**:
Pulleys that are not parallel or aligned properly with the conveyor can cause the belt to run to one side.
- **Out-of-Alignment Idlers**:
Idlers that are not aligned perpendicular to the belt path can create tracking problems.
#### 7.Belt and Splice Quality
- **Poor Belt Quality**:
Substandard belts that do not have uniform thickness or strength can lead to tracking issues.
- **Improper Splicing**:
Incorrectly spliced belts can have uneven surfaces or tensions, causing the belt to misalign.
#### 8. Environmental Factors
- **Temperature Changes**:
Significant changes in temperature can cause the belt material to expand or contract unevenly, leading to misalignment.
- **Contamination**:
Dirt, dust, or other contaminants on the belt or components can affect tracking.
#### 9. Structural Movement
- **Foundation Shifts**:
Movement or settling of the conveyor’s foundation can lead to misalignment of the entire structure.
- **Vibration**:
Excessive vibration from nearby equipment or the conveyor itself can cause components to move out of alignment over time.
### Addressing Belt Misalignment
#### Regular Inspections
- **Routine Checks**:
Regularly inspect the conveyor system for signs of misalignment, wear, or damage. Early detection can prevent more significant issues.
- **Component Inspection**:
Check all pulleys, idlers, rollers, and the belt for proper alignment and condition.
#### Proper Maintenance
- **Cleaning**:
Keep the conveyor belt and components clean to prevent material build-up that can cause misalignment.
- **Lubrication**:
Ensure all moving parts are properly lubricated to reduce wear and friction.
#### Corrective Actions
- **Adjustments**:
Make necessary adjustments to pulleys, idlers, and tensioners to correct any misalignment.
- **Replacement**:
Replace worn or damaged components promptly to maintain proper alignment and operation.
#### Training and Procedures
- **Operator Training**: Train operators and maintenance personnel on proper loading techniques and routine maintenance procedures.
- **Standard Operating Procedures**:
Implement and follow standard operating procedures for conveyor operation and maintenance.
### Conclusion
Understanding the common causes of belt misalignment is crucial for maintaining the efficient and reliable operation of a conveyor system in mineral processing. Regular inspections, proper maintenance, and prompt corrective actions can help prevent misalignment issues, reducing downtime and extending the life of the conveyor belt and components.
Possible Solutions for Belt Misalignment
Addressing belt misalignment in conveyor systems involves a combination of preventive measures, corrective actions, and ongoing maintenance. Here are some effective solutions to ensure proper belt alignment:
#### 1. Correct Installation
- **Ensure Proper Alignment**:
During installation, ensure that all pulleys, idlers, and the conveyor frame are perfectly aligned. Use alignment tools such as laser alignment devices to achieve precise alignment.
- **Level the Frame**:
Make sure the conveyor frame is level and straight. Any deviation can cause belt misalignment.
#### 2. Regular Maintenance and Inspection
- **Routine Checks**:
Conduct regular inspections to identify and address signs of misalignment early. This includes checking the belt, pulleys, idlers, rollers, and other components.
- **Clean Components**:
Keep all parts of the conveyor system clean. Regularly remove any material build-up on pulleys, idlers, and rollers.
- **Lubrication**:
Properly lubricate bearings and other moving parts to reduce friction and wear.
#### 3. Adjustments to Belt Tension
- **Correct Tension**:
Ensure the belt is tensioned according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Both over-tensioning and under-tensioning can cause alignment issues.
- **Even Tension**:
Make sure the tension is even across the width of the belt. Uneven tension can lead to one side being tighter than the other, causing the belt to track off.
#### 4. Proper Loading Practices
- **Even Loading**:
Load materials evenly across the width of the belt. Use loading chutes and hoppers designed to distribute material uniformly.
- **Avoid Impact Loading**:
Minimize the impact of heavy materials falling onto the belt by using impact beds or rollers.
#### 5. Use of Training Idlers
- **Install Training Idlers**:
Training idlers, also known as self-aligning idlers, can help correct minor misalignment automatically. These idlers pivot and tilt to guide the belt back into proper alignment.
- **Strategic Placement**:
Place training idlers at intervals along the conveyor, particularly in areas prone to misalignment such as near the head and tail pulleys.
#### 6. Alignment Devices and Sensors
- **Laser Alignment Tools**:
Use laser alignment tools during installation and maintenance to ensure precise alignment of all components.
- **Tracking Sensors**: Install tracking sensors that detect misalignment and provide real-time alerts, allowing for quick corrective action.
#### 7. Modify and Maintain Conveyor Structure
- **Reinforce the Frame**:
Strengthen and reinforce the conveyor frame to prevent structural movement that can lead to misalignment.
- **Foundation Stability**:
Ensure the conveyor’s foundation is stable and does not shift over time. Address any ground movement or settling issues promptly.
#### 8. Corrective Actions for Worn Components
- **Replace Worn Idlers and Rollers**:
Regularly check and replace any worn or damaged idlers and rollers. Ensure they are properly aligned during replacement.
- **Repair or Replace Damaged Belts**:
Inspect the belt for tears, fraying, or other damage. Repair or replace the belt as necessary to ensure it runs true. #### 9. Implementing Belt Tracking Systems
- **Edge Guide Rollers**:
Install edge guide rollers that keep the belt centered by providing a physical barrier on the belt edges.
- **Crowned Pulleys**:
Use crowned pulleys, which have a slightly higher center, to help guide the belt towards the center.
#### 10. Training and Standard Operating Procedures
- **Operator Training**:
Train operators and maintenance personnel on proper conveyor operation, loading techniques, and routine maintenance procedures.
- **Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)**:
Develop and implement SOPs for all aspects of conveyor operation and maintenance. Ensure that these procedures are followed consistently.
### Conclusion
Addressing belt misalignment requires a comprehensive approach that includes proper installation, regular maintenance, and immediate corrective actions when issues arise. By implementing these solutions, you can ensure that your conveyor system operates efficiently, with minimal downtime and reduced wear on the belt and components.
Proper alignment not only enhances the performance of the conveyor system but also extends its lifespan, providing long-term benefits in mineral processing operations.
Tracking Problems and Their Impact on Operating cost
Tracking problems in conveyor systems can lead to significant and unnecessary expenses, affecting overall efficiency and increasing operational costs. Below are the main areas where tracking problems cause financial impact:
#### 1. Material Waste
- **Spillage**:
Misaligned belts can cause material to spill off the sides, leading to significant material loss.
- **Contamination**:
Spilled material can mix with other materials or contaminants, rendering it unusable.
#### 2. Maintenance Costs
- **Frequent Repairs**:
Continuous misalignment leads to excessive wear and tear on the belt and components, necessitating frequent repairs.
- **Increased Downtime**:
Unscheduled maintenance and repairs disrupt operations, leading to costly downtime.
#### 3. Clean-Up Costs
- **Labor**:
Regular clean-up of spilled materials requires additional labor, increasing labor costs.
- **Equipment**:
Specialized equipment may be needed to clean up spilled material, adding to operational expenses.
#### 4. Component Damage / Failure
- **Idlers and Rollers**:
Misalignment puts extra stress on idlers and rollers, causing premature wear and failure.
- **Bearings**:
Excessive lateral forces on bearings can lead to overheating and failure, requiring replacement.
#### 5. Structure Damage
- **Frame Wear**:
A misaligned belt can rub against the conveyor frame, causing wear and structural damage over time.
- **Support Structures**:
The additional forces exerted by a misaligned belt can lead to bending or breaking of support structures.
### Solutions to Mitigate Tracking Problems and Reduce Expenses
Implementing effective solutions to address tracking problems can help mitigate these costs and improve the overall efficiency of the conveyor system. #### Material Waste Reduction
- **Improved Loading Systems**:
Ensure even distribution of material onto the belt to prevent spillage. Use loading chutes and hoppers designed for uniform loading.
- **Belt Skirting**:
Install belt skirting along the sides to contain materials and prevent spillage.
#### Maintenance Cost Reduction
- **Regular Inspections**:
Conduct regular inspections to identify and address alignment issues before they cause significant damage.
- **Preventive Maintenance**:
Implement a preventive maintenance program that includes routine checks and timely repairs.
#### Clean-Up Cost Reduction
- **Automated Cleaning Systems**: Use belt cleaners and scrapers to automatically remove material buildup and reduce manual clean-up efforts.
- **Spillage Containment**:
Install containment systems such as catch pans or skirts to collect and manage spilled material efficiently. #### Component Damage Mitigation
- **Quality Components**:
Use high-quality, durable components that can withstand the stresses of a misaligned belt.
- **Alignment Devices**:
Install tracking and alignment devices to maintain proper belt alignment and reduce component wear.
#### Structure Damage Prevention
- **Proper Installation**:
Ensure the conveyor frame and support structures are properly aligned and installed to prevent wear and damage.
- **Regular Structural Checks**:
Conduct regular inspections of the conveyor structure to identify and repair any damage caused by misalignment.
### Proactive Measures for Long-Term Benefits #### Training and Procedures
- **Operator Training**:
Train operators on the importance of proper loading, belt tracking, and maintenance procedures.
- **Standard Operating Procedures**:
Develop and implement SOPs for conveyor operation and maintenance to ensure consistent practices.
#### Advanced Monitoring Systems
- **Sensors and Automation**:
Use sensors to monitor belt alignment in real-time and automate corrective actions.
- **Data Analytics**:
Analyze operational data to predict and prevent tracking issues, optimizing maintenance schedules.
### Conclusion
Addressing belt tracking problems is crucial for minimizing unnecessary expenses and ensuring the efficient operation of conveyor systems in mineral processing.
By implementing targeted solutions for reducing material waste, maintenance costs, clean-up costs, component damage, and structure damage, you can significantly improve the reliability and cost-effectiveness of your conveyor operations. Proactive measures, such as regular inspections, proper maintenance, and advanced monitoring, further enhance these benefits, leading to long-term operational success.
Precautions for Maintenance Personnel
To ensure the safety of maintenance personnel working on conveyor systems, it's crucial to follow strict safety protocols and guidelines. Here are key precautions to observe:
1. **Do Not Perform Maintenance While the Conveyor is Operating**
- **Safety First**:
Always prioritize safety and ensure the conveyor is completely stopped before beginning any maintenance tasks.
2. **Lockout/Tagout Procedures**
- **Lock Out the Circuit Breaker**:
Use personal padlocks to lock out the circuit breaker disconnect switch. This ensures the conveyor cannot be accidentally restarted during maintenance.
- **Tagout**:
Place a tag on the switch indicating that maintenance is being performed and the system should not be energized.
3. **Avoid Contact with Moving Parts**
- **No Touching**:
For tasks such as belt tracking or listening for bearing noise, never touch a moving belt, roller, pulley, or bearing. Always use tools or instruments designed for such inspections.
- **Observation**:
Perform visual inspections and listen for unusual noises from a safe distance.
4. **External Inspections and Adjustments**
- **Stay Outside**:
All inspections and adjustments should be performed from outside the conveyor structure. This minimizes the risk of injury from moving parts.
- **Use Proper Tools**:
Utilize appropriate tools and devices for remote inspections and adjustments. 5. **No Reaching Under or Into Running Conveyors**
- **Hands Off**: Never reach under or into the conveyor when the belt is running. Moving parts can cause serious injury.
- **Physical Barriers**:
Use physical barriers or guards to prevent accidental contact with moving parts during maintenance.
6. **Clear Personnel Before Restarting**
- **Safety Check**:
Before restarting the conveyor, ensure all personnel are clear of moving parts and have moved to a safe location.
- **Communication**:
Communicate clearly with all team members to confirm that the conveyor area is clear and it is safe to restart the system.
7. **Maintain Good Housekeeping**
- **Clean Work Area**:
Maintain a clean and organized work area around the conveyor at all times. This reduces the risk of tripping, slipping, and other accidents.
- **Remove Debris**:
Regularly remove debris and ensure walkways and access points are clear.
### Additional Safety Measures
#### Training and Awareness
- **Comprehensive Training**:
Provide thorough training for all maintenance personnel on safety protocols, lockout/tagout procedures, and the specific hazards associated with conveyor systems.
- **Regular Refresher Courses**:
Conduct regular refresher courses to keep safety knowledge up to date. #### Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- **Use Appropriate PPE**:
Ensure maintenance personnel wear the necessary PPE, such as gloves, safety glasses, hard hats, and steel-toed boots.
- **Inspect PPE**: Regularly inspect PPE to ensure it is in good condition and provides adequate protection.
#### Emergency Procedures
- **Emergency Stop Mechanisms**:
Familiarize all personnel with the location and operation of emergency stop mechanisms.
- **First Aid Training**:
Provide first aid training and ensure that first aid supplies are readily accessible.
### Conclusion
Adhering to these safety precautions is essential for protecting maintenance personnel from the inherent dangers associated with conveyor systems. By implementing strict lockout/tagout procedures, avoiding contact with moving parts, performing external inspections and adjustments, maintaining clear communication, and ensuring a clean work environment, you can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and injuries. Continuous training, proper use of PPE, and well-defined emergency procedures further enhance workplace safety.
Additional Precautions for Maintenance Personnel
To further ensure the safety of maintenance personnel working on conveyor systems, the following additional precautions should be observed:
1. **Clean Up Spilled Materials and Lubricants Promptly**
- **Immediate Clean-Up**:
Quickly clean up any spilled materials or lubricants to prevent slips and falls, which can cause injuries.
2. **Replace Safety Guards and Protective Devices**
- **Reinstallation**:
Always replace safety guards and protective devices before putting the conveyor back in service. This ensures that all safety mechanisms are in place to protect against moving parts.
- **Verification**:
Double-check that all guards are properly installed and secured before restarting the conveyor.
3. **Do Not Run the Conveyor with Open or Missing Chain Drive Guards**
- **Safety First**:
Never operate the conveyor with chain drive guards open or missing. These guards are essential for preventing contact with moving parts and reducing the risk of injury.
4. **Stay Alert for Hazardous Conditions**
- **Vigilance**:
Maintenance personnel should always be alert and aware of their surroundings, looking out for hazardous conditions such as loose materials, faulty equipment, or unsafe practices.
5. **Remove Sharp Edges and Protruding Objects**
- **Safety Measures**:
Remove or mitigate sharp edges and protruding objects to prevent injuries. Replace broken or worn parts promptly to maintain a safe working environment.
6. **Manage Air Hoses and Drop Cords Properly**
- **Avoid Tripping Hazards**:
When using air hoses and drop cords, string them overhead or along designated paths to avoid creating tripping hazards.
7. **Stop the Conveyor to Clear Jams or Remove Foreign Objects** - **Safety Procedure**:
Always stop the conveyor before attempting to clear jams or remove foreign objects. This prevents accidental contact with moving parts.
8. **Use Proper Tools and Storage**
- **Tool Usage**:
Use the correct tool for each job to avoid accidents or damage. Carry tools in a pouch or toolbox; never carry tools in pockets, as this can cause injuries.
9. **Wear Goggles While Using Compressed Air**
- **Eye Protection**:
Always wear goggles when using compressed air to protect your eyes from debris and particles.
10. **Safe Use of Compressed Air**
- **No Direct Air Streams**:
Do not direct the stream of compressed air toward yourself or other workers. This can cause serious injuries.
- **No Cleaning with Air**:
Do not use compressed air to clean yourself or your clothing. Use appropriate cleaning methods instead.
- **Avoid Horseplay**:
Horseplay with compressed air is extremely dangerous and can result in serious injuries. Avoid such activities at all times.
11. **Avoid Smoking with Solvents or Cleaning Fluids**
- **Fire Hazard**:
Do not smoke while using solvents or cleaning fluids, as these substances can be highly flammable.
12. **Report Accidents and Irregularities Promptly**
- **Immediate Reporting**:
Report all accidents resulting in personal injury or damage to equipment or material, and any irregularities in equipment operation, promptly to the proper authority. This ensures that issues are addressed quickly and appropriately.
### Conclusion
Following these additional precautions can greatly enhance the safety of maintenance personnel working on conveyor systems. Prompt clean-up of spills, proper use of tools and protective equipment, vigilant observation for hazards, and adherence to safety protocols all contribute to a safer working environment. Ensuring that safety guards are in place, stopping the conveyor to address issues, and reporting accidents and irregularities are crucial steps in maintaining a safe and efficient operation.
Precautions for Operating Personne
To ensure the safe and efficient operation of conveyor systems, operating personnel must follow strict safety protocols.
Here are essential precautions for operating personnel:
1. **Motor Guards in Position**
- **Safety Guards**:
Do not operate the conveyor without the motor guards in position. These guards protect against contact with moving parts.
2. **Stop Conveyor for Clearing Jams**
- **Safety First**:
Always stop the conveyor before clearing jams or removing foreign objects to prevent accidental injury from moving parts.
3. **Clear Area of Personnel Before Starting**
- **Safety Check**:
Ensure all personnel are clear of moving parts before starting the conveyor. Conduct a visual inspection to confirm that the area is safe.
4. **Authorized and Trained Personnel Only**
- **Qualified Operators**:
Only authorized and trained personnel should operate the conveyor. Proper training ensures that operators understand safety protocols and operational procedures.
5. **Avoid Loose Clothing and Accessories**
- **Dress Code**:
Do not wear loose clothing or accessories that could be caught in moving parts of the conveyor. Secure long hair and avoid wearing jewelry.
6. **No Eating or Drinking**
- **Focus on Safety**:
Do not eat food or drink when operating the conveyor. This prevents distractions and contamination of the conveyor system.
7. **No Smoking**
- **Fire Hazard**:
Do not smoke when operating the conveyor to prevent fire hazards and ensure a safe working environment.
8. **Avoid Distractions**
- **Stay Focused**:
Avoid distractions when operating the conveyor. Stay focused on the task to ensure safe and efficient operation.
9. **Never Place Hands in Moving Parts**
- **Hands-Off**:
Never place hands in moving parts when the conveyor is operating. Avoid touching a moving belt to prevent serious injuries.
10. **Keep Conveyor Retracted When Not in Use**
- **Idle Position**:
Keep the conveyor fully retracted and the belt stopped when not in use. This minimizes wear and tear and prevents unauthorized use.
### Additional Safety Measures
#### Regular Training and Refresher Courses
- **Ongoing Training**:
Provide regular training and refresher courses for operating personnel to keep safety knowledge up to date.
- **Emergency Procedures**:
Ensure operators are familiar with emergency stop procedures and the location of emergency stop buttons.
#### Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- **Appropriate PPE**:
Require operators to wear appropriate PPE such as safety glasses, gloves, and hard hats when necessary.
- **PPE Inspection**:
Regularly inspect PPE to ensure it is in good condition and provides adequate protection. #### Communication and Coordination
- **Clear Communication**:
Maintain clear communication among operators and with maintenance personnel to ensure everyone is aware of conveyor status and any potential hazards.
- **Team Coordination**:
Coordinate with other team members, especially during start-up and shut-down procedures, to ensure all safety protocols are followed.
#### Maintenance and Housekeeping
- **Scheduled Maintenance**:
Follow a regular maintenance schedule to ensure the conveyor is in good working condition.
- **Clean Work Area**:
Keep the work area around the conveyor clean and free of obstructions to prevent accidents and ensure smooth operation.
### Conclusion
Following these precautions can significantly enhance the safety and efficiency of conveyor operations. Ensuring that motor guards are in place, stopping the conveyor to address jams, verifying the clearance of personnel, and maintaining focus are all critical steps for safe operation. Proper training, appropriate PPE, clear communication, and regular maintenance further contribute to a safe working environment, protecting both personnel and equipment.
Basic Conveyor Maintenance Checklist
Checklist Maintaining conveyor systems is crucial for ensuring smooth operation, minimizing downtime, and maximizing the lifespan of components.
Here’s a comprehensive checklist covering the essential components of conveyor systems that require regular maintenance:
#### 1. Drives
- **Inspect Motor and Gearbox**:
Check for unusual noise, vibrations, or overheating.
- **Verify Alignment**:
Ensure proper alignment of motor and gearbox with conveyor components.
#### 2. Take-Up Systems
- **Check Tension**:
Verify and adjust tensioning mechanisms to maintain proper belt tension.
- **Inspect Bearings**:
Ensure bearings are lubricated and functioning correctly.
#### 3. Control Equipment
- **Test Operation**:
Regularly test control panels, switches, and emergency stop buttons for proper operation.
- **Calibration**:
Calibrate sensors and control systems as necessary.
#### 4. Belting
- **Inspect Belt Condition**:
Check for signs of wear, damage, or tracking issues.
- **Clean Belts**:
Remove debris and buildup from belts to prevent slippage and damage.
#### 5. Pulleys
- **Inspect Pulley Alignment**:
Ensure pulleys are aligned and free of buildup.
- **Check Lagging**:
Inspect pulley lagging for wear and replace if necessary.
#### 6. Troughing Idlers
- **Inspect Rollers**:
Check rollers for wear, proper rotation, and lubrication.
- **Clean Rollers**:
Remove material buildup to prevent belt tracking issues.
#### 7. Return Idlers
- **Verify Alignment**:
Ensure proper alignment of return idlers to avoid belt mistracking.
- **Inspect Bearings**:
Lubricate bearings and replace if worn or damaged.
#### 8. Tail Sections
- **Inspect Tail Pulleys**:
Check alignment and condition of tail pulleys.
- **Verify Guarding**:
Ensure safety guards are in place to prevent access to moving parts. #### 9. Impact-Loading Equipment
- **Inspect Impact Beds**:
Check for wear and proper alignment of impact beds.
- **Replace Damaged Components**:
Replace damaged impact bars or idlers promptly.
#### 10. Chutes -
**Inspect Chute Liners**:
Check for wear and replace liners as needed.
- **Clear Blockages**:
Ensure chutes are clear of debris to maintain material flow.
#### 11. Skirting
- **Inspect Skirting Seals**:
Check skirting seals for wear and effectiveness.
- **Adjust Position**:
Ensure skirting is properly adjusted to prevent material spillage.
#### 12. Belt Scrapers
- **Inspect Scrapers**:
Check condition and adjustment of belt scrapers.
- **Replace Blades**:
Replace worn scraper blades to maintain effective cleaning.
#### 13. Equipment Guards
- **Verify Guarding**:
Ensure all equipment guards are in place and secure.
- **Inspect for Damage**:
Replace damaged guards to prevent hazards.
#### 14. Covers
- **Check Cover Condition**:
Inspect covers for damage or missing sections.
- **Secure Covers**:
Ensure covers are securely fastened to protect conveyor components.
#### 15. Walkways
- **Inspect Walkway Condition**:
Check walkways for damage or deterioration.
- **Ensure Safety**:
Maintain clear walkways for safe access to conveyor components.
#### 16. Structure
- **Inspect Frame and Supports**:
Check conveyor structure for signs of damage or corrosion.
- **Ensure Stability**:
Verify structural integrity to support conveyor operation.
#### 17. Transfer Stations -
**Inspect Transfers**:
Check alignment and condition of transfer chutes and stations.
- **Clear Blockages**:
Ensure transfers are clear of material buildup to prevent spillage.
#### 18. Specialized Components
- **Site-Specific Equipment**:
Check and maintain specialized components unique to site-specific activities.
- **Follow Manufacturer Guidelines**:
Follow manufacturer recommendations for maintenance of specialized components.
### Maintenance Schedule
- **Regular Inspections**:
Conduct routine inspections of all conveyor components based on manufacturer recommendations and operational conditions.
- **Scheduled Maintenance**:
Implement a scheduled maintenance program to address preventive maintenance tasks and minimize unplanned downtime.
- **Document Maintenance**:
Keep detailed records of maintenance activities, inspections, and any repairs or replacements performed. By following this comprehensive maintenance checklist and schedule, you can ensure that your conveyor system operates efficiently, safely, and reliably, leading to improved productivity and reduced operational costs over its lifespan.
Conveyor Maintenance Checklist - While the System is in Operation
- While the System is in Operation Maintaining and monitoring conveyor systems while they are in operation is essential for identifying potential issues early and ensuring reliable performance.
Here’s a detailed checklist for conducting maintenance checks while the conveyor system is operating:
1. **Regular Walkaround Inspection**
- **Both Sides**:
Walk around both sides of the conveyor system to inspect all moving components.
- **Visual Inspection**:
Note the condition and any unusual behavior of rollers, pulleys, belts, and other moving parts.
- **Listen for Noises**:
Pay attention to any abnormal noises that could indicate issues with bearings or other components.
2. **Material Build-Up**
- **Identify Build-Up**:
Note points where material is accumulating on the conveyor belt or within the system.
- **Clear Build-Up**:
Address material build-up promptly to prevent belt mistracking, increased wear, or operational issues.
3. **Belt Alignment and Tracking**
- **Visual Inspection**:
Look for signs of misalignment or improper belt tracking.
- **Check Tracking Guides**:
Ensure tracking guides are properly adjusted to keep the belt aligned.
4. **Drive Amperage Check**
- **Monitor Amperage**:
Check drive amperage requirements while the conveyor is operating under normal load conditions.
- **Compare with Baseline**:
Compare current amperage levels with historical data for similar loads and conditions.
- **Detect Changes**:
A rise in amperage levels above previous readings may indicate increased drag or resistance within the system.
5. **Action for Increased Amperage**
- **Further Investigation**:
If amperage levels are higher than usual, investigate further when the system is at rest and electrically locked out.
- **Possible Causes**:
Investigate potential causes such as failed bearings, lack of lubrication, or mechanical issues affecting conveyor performance.
### Additional Tips
- **Safety First**:
Always prioritize safety when conducting inspections while the conveyor system is operational. Follow lockout/tagout procedures and use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).
- **Documentation**:
Keep detailed records of maintenance checks, observations, and any corrective actions taken.
- **Regular Training**:
Ensure maintenance personnel are trained in safe inspection practices and understand the operational parameters of the conveyor system.
- **Immediate Action**:
Address any identified issues promptly to prevent further damage and ensure uninterrupted operation of the conveyor system. By following this checklist regularly and proactively addressing any issues observed during operation, you can maintain the efficiency, reliability, and safety of your conveyor system, ultimately optimizing production and minimizing downtime.
Conveyor Maintenance Checklist - While the System is Locked Out
When performing maintenance on a conveyor system that is locked out, it's essential to conduct thorough inspections and address any issues to ensure the system operates efficiently and safely when restarted.
Here’s a detailed checklist for maintenance activities during lockout:
1. **Alignment Check and Adjustments**
- **Verify Alignment**:
Confirm that all conveyor components, including pulleys, idlers, and belts, are in proper alignment.
- **Make Adjustments**:
Adjust tracking guides or alignment settings as needed to prevent belt misalignment during operation.
2. **Inspect and Address Suspect Components**
- **Inspect Rollers and Bearings**:
Closely examine rollers and bearings for signs of wear, damage, or improper rotation.
- **Take Corrective Action**:
Re-lubricate or replace rollers and bearings that are not revolving freely or show signs of wear.
3. **Safety Systems Check**
- **Verify Functionality**:
Check all safety systems such as emergency stop switches, pull cords, and guardrails.
- **Test Operation**:
Test each safety system to ensure they activate correctly and effectively halt conveyor operation in case of emergencies.
4. **Control Equipment Testing**
- **Functionality Check**:
Test control equipment including PLCs, sensors, and motor controls.
- **Calibration**:
Calibrate sensors and control settings as necessary to ensure accurate operation.
5. **Belt Wear Inspection**
- **Check Belt Condition**:
Inspect the entire length of the conveyor belt for wear, especially at edges and splices.
- **Check Stringing**:
Ensure the belt is properly tensioned and not excessively loose or tight (belt stringing).
6. **Loading and Transfer Points**
- **Inspect for Damage**:
Check for signs of damage or wear at loading and transfer points where material impact may occur.
- **Address Issues**:
Repair or replace components at these points to maintain smooth material flow and prevent belt damage.
7. **Chute and Skirting Clearances**
- **Check Clearances**:
Verify clearances between chutes, skirting, and the conveyor belt.
- **Adjust as Needed**:
Adjust skirting and chute configurations to minimize material spillage and maintain effective containment.
8. **Material Build-Up and Spill Cleanup**
- **Remove Build-Up**:
Clear any material build-up on conveyor components such as pulleys, idlers, and rollers.
- **Clean Spills**:
Clean up spills along the conveyor system to prevent material contamination and potential hazards.
### Additional Tips
- **Documentation**:
Document all maintenance activities, inspections, and corrective actions taken during lockout periods.
- **Safety Protocols**:
Follow lockout/tagout procedures rigorously to ensure the safety of maintenance personnel.
- **Training**:
Provide training to maintenance personnel on proper maintenance procedures and safety protocols specific to the conveyor system.
- **Preventive Maintenance**:
Implement a preventive maintenance schedule to regularly inspect and maintain conveyor components, reducing the likelihood of unexpected failures. Performing these maintenance tasks diligently during lockout ensures that the conveyor system operates efficiently, minimizes downtime, and extends the lifespan of components, ultimately contributing to overall operational reliability and safety.
Conveyor Maintenance Checklist - While the System is Locked Out
- While the System is Locked Out During lockout of the conveyor system, thorough maintenance checks and corrective actions are crucial to ensure operational efficiency and safety.
Here’s a detailed checklist for maintenance tasks during lockout periods:
1. **Investigate Causes of Issues**
- **Identify Issues**:
Investigate any observed issues such as belt misalignment, abnormal noise, or component wear.
- **Root Cause Analysis**:
Determine the root causes of these issues to prevent recurrence.
2. **Pillow Block Bearings Lubrication**
- **Follow Manufacturer's Schedule**:
Re-lubricate all pillow block bearings according to the manufacturer’s recommended schedule.
- **Use Recommended Lubricants**:
Use appropriate lubricants suitable for the bearings and operating conditions.
3. **Troughing and Return Rolls Lubrication**
- **Maintenance Schedule**:
Re-lubricate troughing and return rolls per the manufacturer’s recommended schedule or specific installation requirements.
- **Ensure Proper Lubrication**:
Use correct lubrication techniques to ensure smooth operation and longevity of rollers.
4. **Belt Scrapers Inspection**
- **Check Condition**:
Inspect the condition and functionality of belt scrapers.
- **Adjust or Replace**:
Adjust or replace belt scrapers as needed to maintain effective cleaning of the conveyor belt.
5. **Guards and Covers Verification**
- **Ensure Installation**:
Confirm that all guards and covers are securely in place.
- **Safety Compliance**:
Ensure guards and covers meet safety standards and effectively prevent access to moving parts.
6. **Motor Brushes Replacement**
- **Follow Manufacturer's Guidelines**:
Replace motor brushes as specified by the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule.
- **Ensure Correct Replacement**:
Use recommended replacement parts to maintain motor performance and longevity.
### Additional Tips
- **Safety Precautions**:
Adhere to lockout/tagout procedures to ensure the safety of maintenance personnel during inspections and maintenance activities.
- **Documentation**:
Maintain detailed records of maintenance tasks performed, including lubrication schedules, inspections, adjustments, and replacements.
- **Training**:
Provide training to maintenance personnel on the proper techniques for lubrication, inspection, and maintenance of conveyor components.
- **Preventive Maintenance**:
Implement a proactive maintenance schedule to prevent issues and ensure the conveyor system operates reliably.
By following this checklist and conducting thorough maintenance during lockout periods, you can effectively address potential issues, extend the life of conveyor components, and ensure safe and efficient operation of the conveyor system. Regular monitoring and adherence to manufacturer guidelines are key to optimizing conveyor performance and minimizing downtime.
Preventive Maintenance for Conveyors
Implementing preventive maintenance procedures is essential for maintaining the operational efficiency and reliability of conveyor systems.
These procedures help identify potential issues early, allowing corrective action to be taken before failures occur. Here are key preventive maintenance tasks for conveyor systems:
1. **Regular Inspection Schedule**
- **Establish Schedule**:
Set up a regular inspection schedule based on manufacturer recommendations and operational conditions.
- **Visual Inspections**:
Conduct visual inspections of all conveyor components to check for wear, damage, or signs of potential issues.
2. **Lubrication Maintenance**
- **Follow Guidelines**:
Lubricate bearings, rollers, and other moving parts according to the manufacturer’s specifications and recommended schedules.
- **Use Proper Lubricants**:
Ensure the correct type and amount of lubricant are used to prevent premature wear and maintain smooth operation.
3. **Belt Tracking and Alignment**
- **Monitor Belt Tracking**:
Regularly check belt alignment and tracking to prevent issues such as belt misalignment or premature wear.
- **Adjustment**:
Make necessary adjustments to tracking guides and pulleys to ensure the belt runs smoothly along the conveyor path.
4. **Cleaning and Material Build-Up**
- **Remove Build-Up**:
Clean material build-up from rollers, pulleys, and belts to prevent belt mistracking and excessive wear.
- **Inspect Chutes and Skirting**:
Check and clean chutes and skirting to ensure proper material flow and minimize spillage.
5. **Component Wear and Damage**
- **Inspect Wear Parts**:
Check wear liners, belt scrapers, and impact beds for wear and damage.
- **Replace as Needed**:
Replace worn components promptly to prevent deterioration and maintain conveyor performance.
6. **Safety Systems Check**
- **Test Safety Devices**:
Regularly test emergency stop switches, pull cords, and safety guards to ensure they function correctly.
- **Verify Guarding**:
Confirm all guards and covers are securely in place and meet safety standards to protect personnel from moving parts.
7. **Electrical and Control Systems**
- **Inspect Electrical Connections**:
Check wiring and connections for signs of wear, corrosion, or loose connections.
- **Functional Testing**:
Test control panels, PLCs, sensors, and motor controls to verify proper operation and responsiveness.
8. **Documentation and Record-Keeping**
- **Maintain Records**:
Keep detailed records of maintenance activities, inspections, and any repairs or replacements performed.
- **Track Maintenance History**:
Use maintenance records to track trends, identify recurring issues, and schedule future preventive maintenance tasks.
### Benefits of Preventive Maintenance
- **Reduced Downtime**:
Proactively addressing potential issues helps minimize unplanned downtime due to equipment failures.
- **Extended Equipment Life**:
Regular maintenance extends the lifespan of conveyor components, reducing replacement costs.
- **Improved Safety**:
Ensuring safety systems and guards are in place enhances workplace safety for personnel operating and maintaining the conveyor system.
- **Optimized Performance**:
By maintaining equipment in optimal condition, conveyor systems operate more efficiently, contributing to overall production efficiency.
Implementing a comprehensive preventive maintenance program not only improves the reliability and longevity of conveyor systems but also contributes to a safer and more productive working environment.
Regular inspections, proper lubrication, timely repairs, and diligent record-keeping are essential elements of effective preventive maintenance for conveyors.
Preventive Maintenance Checklists for Conveyors
Preventive maintenance is crucial for ensuring conveyor systems operate at maximum efficiency and reliability while minimizing costly repairs and downtime.
Here are three essential categories of preventive maintenance checklists tailored for conveyor systems:
#### 1. Inspection Checklists
Inspection checklists focus on visually inspecting conveyor components for wear, damage, alignment issues, and safety hazards. These inspections help identify potential issues early, allowing for timely repairs or adjustments.
- **Belt and Components Inspection**
- Check belt condition for wear, cuts, or damage.
- Inspect pulleys, rollers, and idlers for wear, proper alignment, and free rotation.
- Verify belt tracking and adjust if necessary.
- Inspect bearings for lubrication and wear.
- Examine chutes and skirtboards for wear and buildup.
- **Safety and Guarding Inspection**
- Verify all safety guards are securely in place and functioning properly.
- Test emergency stop switches and pull cords for immediate response.
- **Electrical Inspection**
- Check electrical connections and control panels for signs of wear or damage.
- Test control systems, sensors, and actuators for proper operation.
#### 2. Cleaning and Lubricating Checklists
Cleaning and lubricating checklists ensure that conveyor components are kept clean and properly lubricated to prevent premature wear and maintain efficient operation.
- **Cleaning Checklist**
- Remove material buildup from belts, pulleys, rollers, and chutes.
- Clean debris and spillage along the conveyor path.
- Ensure proper housekeeping around the conveyor area.
- **Lubrication Checklist**
- Lubricate bearings according to manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Apply appropriate lubricants to pulleys, rollers, and other moving parts.
- Check and refill lubrication reservoirs as needed.
#### 3. Routine Preventive Maintenance Checklists
Routine preventive maintenance checklists encompass scheduled tasks aimed at ensuring overall conveyor system reliability and performance.
- **Scheduled Maintenance Tasks**
- Replace worn components such as belt scrapers, impact beds, and wear liners.
- Adjust belt tension and tracking mechanisms.
- Inspect and replace damaged or worn-out belts.
- **Bearing and Motor Maintenance**
- Inspect and replace pillow block bearings as per manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Check motor brushes and replace if worn out.
- Verify alignment of drives and pulleys.
### Benefits of Using Preventive Maintenance Checklists
- **Enhanced Equipment Lifespan**:
Regular inspections and maintenance tasks help extend the life of conveyor components.
- **Reduced Downtime**:
Proactively addressing issues prevents unexpected breakdowns and reduces downtime.
- **Improved Safety**:
Ensuring safety systems are functional and guards are in place enhances workplace safety.
- **Cost Savings**:
Minimizing repairs and extending equipment life reduces overall maintenance costs. By implementing and following these preventive maintenance checklists, maintenance personnel can effectively manage conveyor systems, optimize performance, and ensure continuous operation with minimal disruption. Regular documentation of maintenance activities and adherence to manufacturer guidelines are key to a successful preventive maintenance program.
Preventive Maintenance - Inspection Checklists
- Inspection Checklists Preventive maintenance inspection checklists are critical for ensuring conveyor systems operate efficiently and reliably over extended periods. These checklists focus on inspections and adjustments that require mechanical and electrical expertise.
Here’s a breakdown of activities and recommended inspection intervals:
#### Activities Covered
- **Visual Inspection**:
Thoroughly examine conveyor components for wear, damage, alignment issues, and safety hazards.
- **Adjustments**:
Make necessary adjustments to ensure optimal performance and prevent premature wear.
- **Tightening**:
Tighten bolts, nuts, and fasteners as needed to maintain structural integrity.
- **Cleaning**:
Remove debris and buildup from components to prevent operational issues.
- **Lubrication**:
Apply lubricants to moving parts according to manufacturer specifications.
#### Recommended Inspection Intervals
1. **Weekly Inspections**
- Conduct basic visual inspections of conveyor components.
- Check for any signs of wear, misalignment, or abnormal noise.
- Verify the functionality of safety systems and emergency stop controls.
2. **Monthly Inspections**
- Perform detailed inspections of belt condition, rollers, pulleys, and bearings.
- Inspect electrical connections and control panels for signs of wear or corrosion.
- Lubricate bearings and moving parts as per schedule.
3. **Quarterly Inspections**
- Check alignment of drive components and pulleys.
- Inspect belt tracking and adjust if necessary.
- Verify the condition of wear liners, chutes, and skirtboards.
4. **Semi-Annual Inspections**
- Conduct comprehensive inspections of all conveyor components.
- Test and calibrate sensors, actuators, and control systems.
- Replace worn-out components such as belt scrapers, impact beds, and wear liners.
5. **Annual Inspections**
- Perform thorough inspections of structural integrity and support systems.
- Evaluate overall conveyor system performance and efficiency.
- Plan for major overhauls or replacements based on inspection findings.
#### Safety Precautions
- **Safety First**:
Never touch moving belts or rotating parts during inspections.
- **Lockout/Tagout**:
Always follow lockout/tagout procedures to ensure safety when working on conveyor systems.
Use appropriate tools and equipment for inspections and adjustments.
### Benefits of Inspection Checklists
- **Early Issue Detection**:
Identify potential issues early before they escalate into costly failures.
- **Improved Reliability**:
Ensure conveyor systems operate efficiently with minimal downtime.
- **Safety Compliance**:
Maintain safe working conditions for maintenance personnel.
- **Cost Savings**:
Reduce repair costs and extend equipment lifespan through proactive maintenance.
By adhering to these preventive maintenance inspection checklists at specified intervals, maintenance personnel can effectively manage and optimize conveyor system performance, ensuring reliable operation and minimizing disruptions in production.
Regular documentation of inspection findings and maintenance activities is essential for tracking equipment condition and planning future maintenance tasks.
Preventive Maintenance: Cleaning and Lubricating Checklists
Cleaning and Lubricating Checklists Cleaning and lubricating checklists are essential for maintaining the operational efficiency and longevity of conveyor systems.
These checklists focus on tasks such as cleaning, lubrication, and minor adjustments that help prevent premature wear and ensure smooth operation.
Here’s a detailed overview:
#### Activities Covered
- **Cleaning**:
Remove debris, dust, and material buildup from conveyor components to prevent operational issues and ensure proper functioning.
- **Lubrication**:
Apply appropriate lubricants to bearings, rollers, pulleys, and other moving parts to reduce friction and wear.
- **Tightening**:
Check and tighten bolts, nuts, and fasteners to maintain structural integrity and prevent loosening during operation.
#### Technical Skill Requirements
- **Moderate Technical Skill**:
Cleaning and lubricating activities do not require as high a level of technical expertise as inspection tasks.
- **Routine Maintenance**:
These tasks focus on routine upkeep to keep conveyor systems operating smoothly between more comprehensive inspections.
#### Recommended Performance Frequencies
1. **Monthly Cleaning and Lubrication**
- Clean debris and buildup from conveyor belts, rollers, and pulleys.
- Lubricate bearings, rollers, and other moving parts according to manufacturer recommendations.
- Check and tighten bolts and fasteners as needed.
2. **Quarterly Cleaning and Lubrication**
- Perform detailed cleaning of conveyor components, including chutes, skirting, and loading points.
- Apply grease or lubricants to drive chains, sprockets, and gearboxes as required.
- Inspect and clean any filters or screens associated with lubrication systems.
3. **Semi-Annual Cleaning and Lubrication**
- Clean and inspect the entire length of the conveyor belt for wear and contamination.
- Lubricate motor bearings and any exposed shaft bearings. - Check alignment of drive components and adjust if necessary.
4. **Annual Cleaning and Lubrication**
- Conduct thorough cleaning of conveyor support structures and walkways.
- Inspect and clean conveyor enclosures, guards, and covers.
- Verify lubrication systems and replace filters or lubricants as needed.
#### Safety Precautions
- **Safety Gear**:
Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves and safety glasses, when performing cleaning and lubricating tasks.
- **Lockout/Tagout**:
Always follow lockout/tagout procedures to ensure safety when accessing conveyor components.
- **Proper Tools**:
Use correct tools and equipment for cleaning, lubricating, and tightening operations.
### Benefits of Cleaning and Lubricating Checklists
- **Extended Equipment Life**:
Regular lubrication reduces friction and wear on conveyor components, extending their lifespan.
- **Improved Efficiency**:
Clean components ensure smooth operation and minimize downtime due to malfunctions.
- **Cost Savings**:
Preventive maintenance reduces the need for costly repairs and replacements.
- **Enhanced Safety**:
Proper maintenance improves workplace safety by reducing the risk of accidents related to equipment malfunction.
By adhering to these cleaning and lubricating checklists at specified intervals, maintenance personnel can effectively manage conveyor system upkeep, ensuring reliable operation and maximizing productivity.
Regular documentation of maintenance activities and adherence to manufacturer guidelines are crucial for maintaining equipment warranties and optimizing conveyor performance.
Preventive Maintenance: Routine Preventive Maintenance Checklists
Routine Preventive Maintenance Checklists Routine preventive maintenance checklists encompass a range of activities that ensure conveyor systems operate smoothly and reliably.
These checklists include tasks that are less complex than those on inspection checklists but more involved than cleaning and lubricating tasks.
Here’s an overview:
#### Activities Covered
- **Daily Maintenance**
- Conduct visual inspections of conveyor belts, rollers, and pulleys for any visible issues.
- Check for abnormal noises or vibrations during operation.
- Verify emergency stop switches and safety systems are functional.
- **Weekly Maintenance**
- Inspect and adjust belt tension to maintain proper alignment and tracking.
- Clean and inspect drive chains, sprockets, and gearboxes for wear and lubricate as needed.
- Check conveyor supports and structural integrity.
- **Biweekly Maintenance**
- Clean and inspect loading and transfer points for material buildup and wear.
- Verify alignment of idlers and rollers along the conveyor path.
- Inspect and tighten all bolts, nuts, and fasteners on conveyor components.
#### Technical Skill Requirements
- **Moderate Skill Level**:
Routine preventive maintenance tasks require familiarity with conveyor systems and mechanical skills for adjustments and minor repairs.
- **Maintenance Oversight**:
These tasks ensure ongoing operational efficiency and identify potential issues before they escalate.
#### Performance Frequencies
1. **Daily Tasks**
- Perform visual inspections of conveyor components and safety systems.
- Check for any signs of wear, misalignment, or abnormal operation. - Verify emergency stop functionality and accessibility.
2. **Weekly Tasks**
- Inspect and adjust belt tension and tracking mechanisms.
- Clean and lubricate drive chains, sprockets, and bearings. - Check alignment of drive components and pulleys.
3. **Biweekly Tasks**
- Clean and inspect all transfer points, chutes, and loading areas.
- Verify tightness of bolts and fasteners on all conveyor components.
- Conduct visual inspections of support structures and walkways.
#### Safety Precautions
- **Safety Awareness**:
Maintain awareness of safety protocols and procedures during maintenance tasks.
- **Personal Protective Equipment**:
Wear appropriate PPE, including gloves and safety glasses, when working on conveyor systems.
- **Lockout/Tagout**:
Always follow lockout/tagout procedures to ensure safety when performing maintenance activities.
### Benefits of Routine Preventive Maintenance Checklists
- **Proactive Maintenance**:
Addressing issues promptly reduces the risk of equipment failure and unplanned downtime.
- **Improved Efficiency**:
Well-maintained conveyor systems operate more efficiently, contributing to overall production efficiency.
- **Cost Savings**:
Regular maintenance reduces repair costs and extends the lifespan of conveyor components.
- **Enhanced Safety**:
Proper maintenance practices create a safer working environment for maintenance personnel and operators.
By implementing and following routine preventive maintenance checklists at specified intervals, maintenance personnel can effectively manage conveyor system upkeep, ensuring reliable operation and minimizing disruptions in production. Documentation of maintenance activities and adherence to manufacturer guidelines are essential for tracking equipment condition and planning future maintenance tasks.
Preventive Maintenance: Daily Checklist (Performed by Operator)
Daily preventive maintenance checklists are essential for operators to ensure conveyor systems operate safely and efficiently.
These tasks focus on routine checks and cleaning to maintain optimal performance. Here’s a detailed checklist for daily maintenance:
#### Operator Responsibilities
1. **Check Operation of Conveyor Controls**
- Verify that all conveyor controls, including start and stop buttons, are functioning correctly.
- Test emergency stop buttons to ensure immediate response.
2. **Inspect Limit Switches**
- Ensure all limit switches are operational and correctly positioned.
- Test switches to verify they activate and deactivate as intended.
3. **Clean Conveyor Surfaces**
- Remove dust, dirt, and debris from conveyor surfaces using appropriate cleaning tools.
- Clean accumulation of debris from belts, rollers, and other conveyor components.
- Conduct cleaning tasks with the conveyor belt stopped and power isolated (lockout/tagout).
4. **Ensure Proper Belt Tracking**
- Check belt alignment and tracking to prevent misalignment and potential damage. - Adjust tracking guides and rollers as needed to ensure the belt runs smoothly.
#### Safety Precautions
- **Safety Awareness**:
Never touch moving belts or rotating parts during maintenance tasks.
- **Lockout/Tagout**:
Always follow lockout/tagout procedures before performing any cleaning or maintenance activities.
- **Proper Tools**:
Use appropriate cleaning tools and equipment to safely remove debris and clean conveyor surfaces. ### Benefits of Daily Preventive Maintenance
- **Early Issue Detection**:
Regular checks help identify potential problems before they lead to equipment failure or downtime.
- **Improved Safety**:
Ensuring controls and emergency stops function properly enhances workplace safety.
- **Extended Equipment Life**:
Cleaning and maintaining proper belt tracking contribute to longer conveyor life.
- **Operational Efficiency**:
Well-maintained conveyors operate more efficiently, minimizing disruptions in production. By incorporating this daily preventive maintenance checklist into operational routines, operators can help maintain conveyor system reliability, safety, and efficiency. Documentation of daily inspections and adherence to safety protocols are critical for effective maintenance management.
Preventive Maintenance: Weekly Checklist
Weekly preventive maintenance checklists are crucial for ensuring conveyor systems operate safely and efficiently. These tasks focus on more detailed inspections and maintenance activities that help detect potential issues early.
Here’s a comprehensive checklist for weekly maintenance:
#### Safety Precautions
- **Safety First**:
Adhere to all safety protocols and procedures. Always turn off the conveyor before performing inspections or maintenance tasks. Never touch moving belts or rotating parts.
#### Inspection and Maintenance Tasks
1. **Examine Controls and Wiring**
- Shut down the conveyor system and disconnect power.
- Inspect controls, wiring, and conduit for any signs of damage, wear, or loose connections.
- Do not touch exposed wires; instead, secure loose wires and notify maintenance for proper repair.
2. **Inspect Motor and Reducer**
- With the conveyor shut down, visually inspect the motor and reducer housings for any damage or leaks.
- Look for evidence of lubricant leakage from the gear case.
- Check the oil level in the gear case; if low, add lubricant as per manufacturer specifications (e.g., Texaco Multi-gear EP-85W-140 or equivalent).
3. **Belt and Component Inspection**
- Check the condition of conveyor belts for wear, cuts, or damage.
- Inspect pulleys, rollers, and idlers for wear, alignment, and free rotation. - Verify belt tracking and adjust if necessary.
4. **General Inspection**
- Walk along the conveyor path and visually inspect all components for signs of wear, misalignment, or abnormal operation.
- Clean any accumulated debris from conveyor surfaces and components. #### Lubrication
- Lubricate bearings, rollers, and other moving parts according to manufacturer recommendations during weekly inspections.
#### Documentation
- Record inspection findings and any maintenance performed in the maintenance log for reference and future planning.
### Benefits of Weekly Preventive Maintenance
- **Early Detection**:
Identify potential issues early to prevent equipment failures and minimize downtime.
- **Enhanced Safety**:
Regular inspections ensure safety systems and controls are in optimal condition.
- **Extended Equipment Life**:
Proper maintenance and lubrication contribute to longer conveyor system lifespan.
- **Operational Efficiency**:
Well-maintained conveyors operate efficiently, supporting consistent production output. By following this weekly preventive maintenance checklist, maintenance personnel can effectively manage conveyor system upkeep, ensuring reliable operation and safety. Regular documentation of maintenance activities and adherence to manufacturer guidelines are essential for maximizing conveyor performance and longevity.
Preventive Maintenance: Weekly Checklist
Weekly Checklist
Weekly preventive maintenance checklists ensure conveyor systems operate smoothly and safely by addressing cleaning and minor maintenance tasks.
Here’s a detailed checklist for weekly maintenance:
#### Cleaning and Maintenance Tasks
1. **Clean Conveyor Surfaces**
- Ensure the conveyor is properly locked out and power is disconnected. - Remove any accumulated debris, dirt, or material from beneath the conveyor surfaces.
- Use appropriate cleaning tools and equipment to clean conveyor belts, rollers, and components.
2. **Restore Conveyor**
- After cleaning, restore the conveyor to its original operational status.
- Ensure all inspection equipment and tools are removed from the work area. - Verify that all safety guards and covers are securely in place.
3. **Initiate Repair Work Orders**
- Identify any maintenance issues or deficiencies observed during the inspection.
- Initiate repair work orders for any required repairs or replacements.
- Document and prioritize repairs based on urgency and impact on conveyor operation.
4. **Reporting**
- Report any serious deficiencies or safety concerns to the maintenance supervisor immediately.
- Provide detailed information and observations to facilitate prompt action and resolution.
#### Safety Precautions
- **Lockout/Tagout**:
Always lock out and tag out the conveyor system before performing any maintenance or cleaning tasks.
- **Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)**:
Wear appropriate PPE, including gloves and safety glasses, when cleaning conveyor components.
- **Safety Awareness**:
Maintain awareness of potential hazards and follow established safety procedures at all times. ### Benefits of Weekly Preventive Maintenance
- **Operational Efficiency**:
Regular cleaning and maintenance help prevent buildup and ensure smooth operation.
- **Safety**: Proper maintenance reduces the risk of accidents and ensures compliance with safety regulations.
- **Equipment Longevity**:
Cleaning and minor repairs extend the lifespan of conveyor components.
- **Cost Savings**:
Preventive maintenance minimizes the need for major repairs and costly downtime. By following this weekly preventive maintenance checklist, operators and maintenance personnel can contribute to the reliability and efficiency of conveyor systems. Documenting maintenance activities and promptly addressing repair needs are essential for maintaining optimal conveyor performance.
Preventive Maintenance: Monthly Checklist
Monthly Checklist Monthly preventive maintenance checklists focus on more detailed inspections and specific maintenance tasks to ensure conveyor systems operate efficiently and reliably.
Here’s a comprehensive checklist for monthly maintenance:
#### Inspection and Maintenance Tasks
1. **Examine Pulleys and Bearings**
- While the conveyor is running, listen for any abnormal noises coming from pulley assemblies or bearings.
- Use a metal rod to transmit sound to your ear to pinpoint the source of abnormal noise.
- Never reach under or into the conveyor when the belt is running; always ensure the conveyor is properly locked out and tagged out.
2. **Lubrication of Pulley Bearings**
- Lubricate all pulley bearings according to manufacturer recommendations, typically every four to six weeks.
- Tighten setscrews on pulleys as needed to prevent loosening during operation.
3. **Accessing Pulleys**
- Some pulleys may require removing covers in mating boom sections for access.
- Use a metal rod to reach through access windows to contact and inspect bearings safely.
#### Safety Precautions
- **Safety First**:
Follow lockout/tagout procedures before inspecting or maintaining conveyor components.
- **Personal Protective Equipment**:
Wear appropriate PPE, including safety glasses and gloves, when handling tools and conducting inspections.
- **Equipment Shutdown**: Never perform maintenance tasks or inspections on moving or rotating parts of the conveyor.
### Benefits of Monthly Preventive Maintenance
- **Early Issue Detection**:
Regular inspections help identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems.
- **Improved Efficiency**:
Properly maintained pulleys and bearings contribute to smoother conveyor operation.
- **Extended Lifespan**:
Regular lubrication and maintenance extend the life of conveyor components.
- **Safety Compliance**:
Adhering to safety protocols ensures a safe working environment for maintenance personnel.
By adhering to this monthly preventive maintenance checklist, maintenance personnel can effectively manage conveyor system upkeep, ensuring reliable operation and minimizing downtime.
Documenting maintenance activities and promptly addressing repair needs are essential for maintaining optimal conveyor performance and safety standards.
Preventive Maintenance: Monthly Checklist
Monthly preventive maintenance for conveyor systems involves detailed inspections and specific tasks to ensure operational efficiency and reliability.
Here’s a comprehensive checklist focusing on examining belts and return rollers:
#### Inspection and Maintenance Tasks
1. **Examine Belt**
- While the conveyor is running, visually inspect the belt for any signs of damage, such as cuts, tears, or wear.
- Check belt lacing for any physical damage or signs of wear.
- Remove any ravelled edges or loose cords that could catch on pulley assemblies.
- Repair or replace damaged belt lacing promptly to prevent further issues.
- Never perform any maintenance or repair work on the belt while it is in motion; ensure the conveyor is properly locked out and tagged out.
2. **Inspect Return Rollers**
- Use a metal rod to contact the protruding ends of the hex shafts of return rollers to listen for abnormal bearing noises.
- Remove window covers, if necessary, to gain access to roller shafts for inspection.
- Avoid reaching your hand through access windows or under the conveyor while the belt is running to prevent accidents.
- Replace all covers securely once inspection and maintenance tasks are completed.
#### Safety Precautions
- **Lockout/Tagout**:
Always follow lockout/tagout procedures before conducting any maintenance or inspection on conveyor components.
- **Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)**: Wear appropriate PPE, such as safety glasses and gloves, when handling tools and conducting inspections.
- **Workplace Safety**:
Never reach into or under the conveyor while it is operating to avoid serious injuries. ### Benefits of Monthly Preventive Maintenance
- **Early Problem Detection**:
Regular inspections help identify belt and roller issues early, preventing costly breakdowns and downtime.
- **Improved Belt Performance**:
Prompt repair of damaged belt lacing and edges ensures smooth operation and reduces the risk of belt failures.
- **Extended Equipment Life**:
Proper maintenance of return rollers and belts contributes to longer conveyor system lifespan.
- **Safety Compliance**:
Adhering to safety protocols ensures a safe working environment for maintenance personnel.
By following this monthly preventive maintenance checklist, maintenance personnel can effectively manage conveyor system upkeep, ensuring reliable operation and minimizing disruptions in production.
Documenting maintenance activities and promptly addressing repair needs are crucial for maintaining optimal conveyor performance and safety standards.
Preventive Maintenance: Monthly Checklist
Monthly preventive maintenance for conveyor systems involves thorough inspections and specific tasks to ensure operational reliability and safety.
Here’s a detailed checklist focusing on examining mounting bolts and electrical cable reels:
#### Inspection and Maintenance Tasks
1. **Examine Mounting Bolts**
- Check all drive motors by jogging units to ensure mounting bolts are tight and secure.
- Inspect conveyor hold-down bolts to ensure the conveyor is firmly secured to floor hold-down devices.
- Tighten bolts as necessary to prevent loosening during operation.
2. **Inspect Electrical Cable Reel**
- Examine the electrical cable to ensure it is securely connected and not pulling out from the cable connector.
- Completely extend and retract the conveyor while observing the recoil of the cable.
- If the cable is sagging, fully extend the conveyor and consider adding an additional wrap to the spring at the reel housing to provide proper tension.
- Refer to manufacturer’s literature for guidance on adjusting the spring tension to avoid over-tensioning. #### Safety Precautions
- **Lockout/Tagout**:
Always follow lockout/tagout procedures before inspecting or performing maintenance on conveyor components.
- **Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)**:
Wear appropriate PPE, including gloves and safety glasses, when handling tools and conducting inspections.
- **Equipment Operation**:
Ensure the conveyor is powered off and properly isolated before checking mounting bolts and cable reels.
### Benefits of Monthly Preventive Maintenance
- **Enhanced Reliability**:
Regular inspections and maintenance tasks help prevent equipment failures and reduce downtime.
- **Safety Compliance**:
Properly secured mounting bolts and electrical cables ensure safe operation of the conveyor system.
- **Extended Equipment Life**:
Routine checks and adjustments contribute to longer conveyor system lifespan.
- **Efficient Operation**:
Well-maintained mounting bolts and properly tensioned cables optimize conveyor performance.
By following this monthly preventive maintenance checklist, maintenance personnel can effectively manage conveyor system upkeep, ensuring reliable operation and minimizing disruptions in production.
Documenting maintenance activities and promptly addressing any issues are essential for maintaining optimal conveyor performance and safety standards.
Preventive Maintenance: Monthly Checklist
Monthly preventive maintenance for conveyor systems involves detailed inspections and specific tasks to ensure operational reliability and safety.
Here’s a comprehensive checklist focusing on electrical wiring and cleanup tasks:
#### Inspection and Maintenance Tasks
1. **Inspect Electrical Wiring**
- Check all electrical conduits and fittings for any signs of damage, wear, or deterioration.
- Inspect wiring and connections to ensure they are secure and properly insulated.
- Address any damaged, loose, or bare wiring or connections promptly to prevent electrical hazards.
2. **Cleanup**
- Restore the conveyor system to its original operational status after completing inspections and maintenance tasks.
- Remove all inspection equipment and tools from the work area.
- Initiate repair work orders for any identified issues or deficiencies that require further attention.
- Report any serious deficiencies or safety concerns to the maintenance supervisor immediately for proper resolution.
#### Safety Precautions
- **Lockout/Tagout**:
Always follow lockout/tagout procedures before inspecting or performing maintenance on electrical components.
- **Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)**:
Wear appropriate PPE, including gloves and safety glasses, when handling electrical components and conducting inspections.
- **Electrical Safety**:
Avoid contact with exposed wires or components to prevent electrical shock or injury.
### Benefits of Monthly Preventive Maintenance
- **Preventive Measures**:
Regular inspections help detect and address potential electrical issues before they lead to equipment failure or safety hazards.
- **Safety Compliance**:
Proper maintenance of electrical wiring ensures safe operation of the conveyor system.
- **Equipment Longevity**:
Addressing wiring issues promptly contributes to longer conveyor system lifespan.
- **Operational Efficiency**:
Well-maintained electrical components support reliable and efficient conveyor operation.
By adhering to this monthly preventive maintenance checklist, maintenance personnel can effectively manage conveyor system upkeep, ensuring reliable operation and minimizing disruptions in production. Documenting maintenance activities and promptly addressing repair needs are essential for maintaining optimal conveyor performance and safety standards.
Preventive Maintenance: Quarterly Checklist
Quarterly preventive maintenance for conveyor systems involves more in-depth inspections and adjustments to ensure long-term reliability and performance.
Here’s a detailed checklist focusing on cam roller lubrication and adjustment:
#### Inspection and Maintenance Tasks
1. **Cam Roller Lubrication and Adjustment**
- **Inspect Cam Rollers**:
Check both front and rear cam rollers for wear, damage, or signs of misalignment.
- **Adjust Cam Rollers**:
Ensure all cam rollers are properly adjusted for smooth operation.
- **Lubricate Cam Rollers**:
Front cam support blocks can typically be lubricated without removing guards.
- For rear cam rollers, remove the rear guard to access and lubricate them as needed.
- Use appropriate lubricants recommended by the manufacturer.
- **Lockout/Tagout**:
Always lock out and tag out the conveyor system before performing any maintenance or adjustments.
#### Safety Precautions
- **Lockout/Tagout**:
Ensure the conveyor system is properly locked out and tagged out before starting any maintenance tasks.
- **Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)**:
Wear appropriate PPE, including gloves and safety glasses, when handling tools and conducting inspections.
- **Machine Safety**:
Avoid reaching into or near moving parts of the conveyor system to prevent injuries.
### Benefits of Quarterly Preventive Maintenance
- **Enhanced Performance**:
Regular lubrication and adjustment of cam rollers maintain smooth conveyor operation and minimize wear.
- **Long-Term Reliability**:
Quarterly inspections help identify and address potential issues before they lead to major equipment failures.
- **Safety Compliance**:
Adhering to maintenance procedures ensures safe operation and minimizes workplace hazards.
- **Cost Savings**:
Preventive maintenance reduces the risk of unplanned downtime and costly repairs.
By following this quarterly preventive maintenance checklist, maintenance personnel can effectively manage conveyor system upkeep, ensuring reliable operation and extending the lifespan of critical components. Documenting maintenance activities and promptly addressing any issues identified during inspections are crucial for maintaining optimal conveyor performance and safety standards.
Preventive Maintenance: Semi-Annually Checklist
Semi-annual preventive maintenance for conveyor systems focuses on critical tasks that ensure optimal performance and longevity of gear boxes.
Here’s a detailed checklist for changing fluid in gear boxes:
#### Gear Box Lubrication and Maintenance
1. **Change Fluid in Gear Boxes**
- **Drain and Clean Gear Cases**:
Drain the gear cases completely and clean them to remove any debris or old lubricant.
- **Lubricant Replacement Procedure**:
a. **Remove Oil Level Plug**: Locate and remove the oil level plug on the side of the gear box.
b. **Remove Fill Line Plug**: Remove the fill line plug located on the top of the gear box.
c. **Add Lubrication**: Pour new lubricant through the top fill line port.
d. **Check Fluid Level**: Add lubricant until it reaches the fluid level line hole. Do not over-fill.
e. **Replace Plugs**: Securely replace both the oil level plug and the fill line plug in the gear box.
- **Electrical Lockout**: Always perform gear box maintenance with the conveyor system locked out and tagged out to prevent accidental startup.
#### Safety Precautions
- **Lockout/Tagout**: Ensure the conveyor system is properly locked out and tagged out before performing any maintenance on gear boxes.
- **Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)**: Wear appropriate PPE, such as gloves and safety glasses, when handling tools and lubricants.
- **Gear Box Handling**: Follow manufacturer’s guidelines for handling and disposing of old lubricant.
### Benefits of Semi-Annual Preventive Maintenance
- **Optimal Gear Performance**: Regular lubrication ensures smooth operation and reduces friction in gear boxes.
- **Extended Gear Life**: Changing lubricant semi-annually prevents wear and tear on gear components.
- **Cost Efficiency**: Preventive maintenance minimizes the risk of gear box failures and costly repairs.
- **Safety Compliance**: Adhering to maintenance procedures enhances workplace safety and reduces hazards.
By following this semi-annual preventive maintenance checklist, maintenance personnel can effectively manage conveyor system upkeep, ensuring reliable operation and minimizing downtime. Documenting maintenance activities and adhering to manufacturer’s recommendations are essential for maintaining optimal conveyor performance and safety standards.
Preventive Maintenance: Semi-Annually Checklist
Semi-annual preventive maintenance for conveyor systems involves critical inspections and maintenance tasks to ensure the continued efficiency and reliability of the equipment.
Here’s a detailed checklist focusing on examining the master control panel and observing the drive section:
#### Master Control Panel Inspection
1. **Examine Master Control Panel**
- **Exterior Cleaning**: Wipe dust and debris from the exterior of the master control panel.
- **Interior Cleaning**: Open the panel door and carefully remove dust from the interior using a non-conductive brush or cloth.
- **Inspect Electrical Components**: Avoid touching wires and inspect for any signs of burned wiring or loose terminal connections.
- **Close Panel**: Securely close the panel door after inspection to prevent dust accumulation and protect electrical components.
#### Drive Section Observation
2. **Observe Drive Section**
- **Motor and Reducer Inspection**: While the conveyor is running, use a metal rod to gently contact the motor and reducer housing.
- **Detect Vibration**: Detect excessive vibration from bearings or gears that could indicate wear or damage.
- **Listen for Abnormal Sounds**: Listen attentively for any unusual sounds that may indicate internal parts wear or damage.
- **Safety Precautions**: Do not approach or go near moving parts of the conveyor system during inspection to avoid injury.
#### Safety Precautions
- **Lockout/Tagout**: Ensure the conveyor system is properly locked out and tagged out before performing any maintenance on electrical components or the drive section.
- **Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)**: Wear appropriate PPE, such as gloves and safety glasses, when handling tools and conducting inspections near machinery.
- **Electrical Safety**: Avoid contact with live wires or electrical components to prevent electrical shock hazards. ### Benefits of Semi-Annual Preventive Maintenance
- **Early Problem Detection**: Regular inspections help identify potential issues before they lead to equipment failures or downtime.
- **Improved Equipment Performance**: Cleaning and inspecting the control panel and drive section ensure optimal operation and efficiency.
- **Extended Equipment Lifespan**: Proper maintenance reduces wear and prolongs the life of critical components like motors, reducers, and electrical systems.
- **Safety Compliance**: Adhering to maintenance procedures enhances workplace safety and reduces risks associated with equipment operation.
By following this semi-annual preventive maintenance checklist, maintenance personnel can effectively manage conveyor system upkeep, ensuring reliable operation and minimizing disruptions in production. Documenting maintenance activities and promptly addressing any issues identified during inspections are essential for maintaining optimal conveyor performance and safety standards.
Preventive Maintenance: Semi-Annually Checklist
Semi-annual preventive maintenance for conveyor systems involves critical inspections and maintenance tasks to ensure the continued efficiency and reliability of the equipment.
Here’s a detailed checklist focusing on cleaning boom roller chains, inspecting wheel bearings, and track cleanout for traversing units:
#### Cleaning Boom Roller Chains
1. **Clean Boom Roller Chains**
- **Shutdown and Lockout**:
Ensure the conveyor is shut down and properly locked out to prevent accidental startup.
- **Clean Chains and Sprockets**:
Wipe off dirt and debris from boom roller chains and sprockets using a clean cloth or brush.
- **Lubricate Chains**: Apply SAE #10 weight oil to lubricate the chains, ensuring smooth operation and reducing friction.
#### Wheel Bearing Inspection and Lubrication
2. **Wheel Bearing Inspection**
- **Traversing Units**: If the conveyor is a traversing unit, inspect each wheel bearing for wear, proper alignment, and tightness in the wheel mount.
- **Lubrication Schedule**: Lubricate all wheel bearings at least twice a year. If the unit is traversed regularly, lubricate quarterly for optimal performance.
- **Lockout Requirement**: Always perform wheel bearing inspection and lubrication with the conveyor system locked out to prevent movement.
#### Track Cleanout for Traversing Units
3. **Track Cleanout**
- **Inspect Rear Track**: If the conveyor has a floor-mounted track for traversing, check the rear track for build-up of dirt and debris.
- **Prevent Interference**: Ensure debris does not accumulate to the extent that it interferes with the movement of conveyor wheels.
- **Clean-Out Slots**: Use clean-out slots provided at each end of the track to remove accumulated debris effectively.
#### Safety Precautions
- **Lockout/Tagout**: Ensure the conveyor system is properly locked out and tagged out before performing any maintenance on chains, bearings, or tracks.
- **Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)**: Wear appropriate PPE, such as gloves and safety glasses, when handling tools and lubricants.
- **Equipment Handling**: Avoid reaching into moving parts or placing hands near conveyor components during inspection and maintenance.
### Benefits of Semi-Annual Preventive Maintenance
- **Enhanced Equipment Performance**: Regular cleaning and lubrication of chains and bearings ensure smooth operation and reduce wear.
- **Extended Equipment Lifespan**: Proper maintenance reduces the risk of premature failure and extends the life of conveyor components.
- **Operational Efficiency**: Maintaining clean tracks prevents operational disruptions caused by debris interference.
- **Safety Compliance**: Following maintenance procedures and safety guidelines minimizes workplace hazards associated with conveyor operation.
By following this semi-annual preventive maintenance checklist, maintenance personnel can effectively manage conveyor system upkeep, ensuring reliable operation and minimizing disruptions in production. Documenting maintenance activities and promptly addressing any issues identified during inspections are essential for maintaining optimal conveyor performance and safety standards.
Preventive Maintenance: Lubrication Checklist
Proper lubrication of conveyor components is crucial for ensuring smooth operation and extending the lifespan of critical parts.
Here’s a detailed checklist focusing on lubrication points that require lock-out and accessibility considerations:
#### Lubrication Points
1. **Pillow Block, Take-Up, and Flange Bearings**
- **Identify Bearings**:
Locate pillow block, take-up, and flange bearings holding the main pulley assemblies.
- **Grease Fittings**:
Each bearing should have its own grease fitting, accessible from the front, rear, or sides of the conveyor section.
- **Lubrication Procedure**:
Use standard grease fittings to apply lubricant to each bearing as per manufacturer’s recommendations.
- **Lock-Out Requirement**:
Perform lubrication with the conveyor system locked out to prevent accidental startup.
2. **Cam Rollers and Cam Followers**
- **Purpose**: Cam rollers and cam followers guide and support the booms as they extend and retract.
- **Access Points**: Each cam roller and cam follower should have accessible grease fittings from designated locations (front, rear, or sides).
- **Lubrication Procedure**: Apply grease to cam rollers and cam followers using appropriate lubrication tools and materials.
- **Accessing Rear Cam Rolls**: To lubricate rear cam rollers and followers, remove the rear cover of the machine. Ensure proper safety precautions and lock-out procedures are followed.
#### Safety Precautions
- **Lockout/Tagout**: Always lock out and tag out the conveyor system before performing any lubrication tasks on bearings, cam rollers, or cam followers.
- **Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)**: Wear appropriate PPE, such as gloves and safety glasses, when handling grease and accessing conveyor components.
- **Equipment Handling**: Avoid reaching into moving parts or placing hands near conveyor components during lubrication.
### Benefits of Proper Lubrication
- **Improved Performance**: Proper lubrication reduces friction, wear, and heat generation in bearings and cam rollers, leading to smoother conveyor operation.
- **Extended Component Life**: Regular lubrication extends the lifespan of conveyor components, minimizing downtime and replacement costs.
- **Preventive Maintenance**: Scheduled lubrication prevents equipment failures and ensures continuous operation of the conveyor system.
- **Safety Compliance**: Following lock-out procedures and safety guidelines protects maintenance personnel from injuries and accidents.
By following this lubrication checklist with lock-out procedures, maintenance personnel can effectively manage conveyor system upkeep, ensuring reliable operation and minimizing disruptions in production.
Documenting maintenance activities and adhering to manufacturer’s recommendations are essential for maintaining optimal conveyor performance and safety standards.
Belt Conveyor Inspections Checklist
Here's a comprehensive guide to troubleshooting common conveyor belt problems:
### Conveyor Belt Troubleshooting Guide
#### 1. **Belt Tracking Issues**
- **Symptoms**: Belt mistracking, off-center loading, excessive wear on edges.
- **Possible Causes**:
- Misalignment of idlers or pulleys.
- Uneven tensioning of the belt.
- Build-up of material on idlers or pulleys.
- **Troubleshooting Steps**:
- Inspect and adjust idler and pulley alignment.
- Ensure proper tensioning of the belt.
- Clean idlers and pulleys to remove material build-up.
- Check for any obstructions along the conveyor path.
#### 2. **Belt Slippage**
- **Symptoms**: Belt slipping on drive pulley, reduced conveyor speed.
- **Possible Causes**:
- Insufficient belt tension.
- Contaminated or worn drive pulley surface. - Overloaded conveyor causing excessive torque.
- **Troubleshooting Steps**:
- Increase belt tension as per manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Clean or replace drive pulley surface if contaminated or worn.
- Reduce conveyor load to prevent overloading.
#### 3. **Belt Wear or Damage**
- **Symptoms**: Visible tears, cuts, or gouges on the belt surface.
- **Possible Causes**:
- Material impact or abrasion.
- Misalignment causing friction.
- Excessive tension or load.
- **Troubleshooting Steps**:
- Inspect conveyor for misalignment and correct if necessary.
- Evaluate material handling practices to reduce impact.
- Adjust belt tension to recommended levels.
- Replace damaged sections of the belt promptly.
#### 4. **Excessive Noise or Vibration**
- **Symptoms**: Unusual noise or vibration during conveyor operation.
- **Possible Causes**:
- Misaligned components.
- Loose or worn bearings.
- Improper tensioning of the belt.
- **Troubleshooting Steps**:
- Check and align all conveyor components, including idlers and pulleys.
- Inspect and replace worn or damaged bearings.
- Adjust belt tension and ensure it is uniform throughout the conveyor length.
#### 5. **Material Spillage**
- **Symptoms**: Material falling off the conveyor belt, spillage along the conveyor path.
- **Possible Causes**:
- Inadequate containment at transfer points.
- Misalignment or mistracking of the belt.
- Worn or ineffective scrapers.
- **Troubleshooting Steps**:
- Install or adjust transfer point skirting and containment.
- Ensure belt tracking is accurate and adjust if necessary.
- Replace worn or ineffective scrapers to improve material removal.
#### 6. **Electrical or Control Issues**
- **Symptoms**: Conveyor not starting or stopping properly, erratic operation.
- **Possible Causes**:
- Faulty wiring or connections.
- Malfunctioning control panel or sensors.
- Power supply issues.
- **Troubleshooting Steps**:
- Inspect and test electrical connections and wiring.
- Check control panel for error codes or indicators.
- Verify power supply and ensure it meets conveyor specifications.
#### 7. **Emergency Stop Activation**
- **Symptoms**: Conveyor stops unexpectedly, emergency stop button triggered.
- **Possible Causes**:
- Manual activation of emergency stop button.
- Faulty emergency stop circuit or wiring.
- Overloaded conveyor causing safety shutdown.
- **Troubleshooting Steps**:
- Reset emergency stop button and verify safety conditions.
- Inspect emergency stop circuit for faults or loose connections.
- Reduce conveyor load or address overload conditions to prevent frequent stops.
### General Tips for Conveyor Maintenance
- **Regular Inspections**: Conduct routine inspections and maintenance as per manufacturer guidelines.
- **Proper Lubrication**: Ensure bearings and moving parts are adequately lubricated.
- **Training**: Train operators and maintenance personnel on safe operation and maintenance practices.
- **Documentation**: Keep detailed records of maintenance activities and repairs. By following this troubleshooting guide and implementing preventive maintenance practices, you can minimize downtime, extend conveyor belt life, and optimize operational efficiency in your facility.
Always prioritize safety and consult with qualified technicians or manufacturers for complex issues or repairs.